Translational research on muscle extracellular matrix and nucleus (TREASURE)
Genetics and Pathophysiology of Neuromuscular Diseases Related to the Extracellular Matrix and the Nucleus
Our research interests focus on two groups of neuromuscular disorders (NMD): myopathies due to abnormalities of the myomatrix and of the nucleus. The long-term objective of our work is to propose relevant therapeutic options based on our knowledge of the genetic basis and of the underlying pathomechanisms at play in these rare diseases.
Research Project: Genetics and pathophysiology of neuromuscular disorders linked to the extracellular matrix and to the nucleus
Our team focuses on 2 groups of neuromuscular disorders: myopathies due to the defective myomatrix (collagen VI and other components of the extracellular matrix) and to defects of the myonucleus (Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and other striated muscle laminopathies due to mutations in the laminA/C gene or genes encoding components of nuclear membrane). These myopathies share some clinical features, notably prominent contractures, and constitute differential diagnosis[in1] .
These disorders are highly heterogeneous, clinically and genetically, and to date no treatment is available. Our previous work led us to identify the involvement of various genetic alterations and to develop tools (cellular and animal models) that are crucial for deciphering pathomechanisms, understanding the molecular defects and unveiling therapeutic targets.
We are still facing several challenges and bottlenecks: 1) a number of patients are still awaiting molecular diagnosis; 2) relevant biomarkers are scarce; 3) functions of the involved proteins and underlying pathomechanisms are still poorly understood … We previously have and continue to tackle several transverse processes (e.g. contractile dysfunction, defective mechanosensing, fibrosis …) using our specific expertise (nuclear envelop, nucleoplasm, extracellular matrix…).
Current research axes:
- Definition of genetic and clinical spectrum and delineation of natural history of these NMDs,
- Development of new tools to validate genetic variants identified through NGS (next generation sequencing),
- Deciphering pathomechanisms that affect skeletal and/or cardiac muscle, with the overall goal of identifying and assessing therapeutic options for these disorders.
Our work is carried out on biological material derived from patients (DNA, RNA cultured cells, or muscle biopsies), and on animal models developed in the team (mouse, zebrafish).
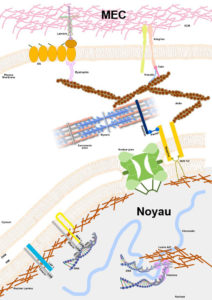
Noyau-MEC ©Astrid Brull
| Name | Position | ORCID |
|---|
Journal articles
- Louise Benarroch, Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Vincent Procaccio, Dalil Hamroun. The 2025 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2025, 46, pp.105261. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2024.105261⟩. ⟨hal-04926625⟩
- Emmanuelle Pion, Gisèle Bonne, Antonio Atalaia, Emmanuelle Salort-Campana, Svetlana Gorokhova, et al.. L’actionnabilité clinique des gènes. Médecine/Sciences, 2024, 40, pp.6-8. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2024128⟩. ⟨hal-04790193⟩
- Gorka Fernández-Eulate, Girolamo Alfieri, Marco Spinazzi, Isabelle Ackermann-Bonan, Fanny Duval, et al.. Phenotype variability and natural history of X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy. Journal of Neurology, 2024, ⟨10.1007/s00415-024-12298-0⟩. ⟨hal-04546595⟩
- Antonio Atalaia, Dagmar Wandrei, Nawel Lalout, Rachel Thompson, Adrian Tassoni, et al.. EURO-NMD registry: federated FAIR infrastructure, innovative technologies and concepts of a patient-centred registry for rare neuromuscular disorders. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2024, 19 (1), pp.66. ⟨10.1186/s13023-024-03059-3⟩. ⟨hal-04460667⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Gisèle Bonne, François Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2024 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2024, 34 (2), pp.126-170. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.12.007⟩. ⟨hal-04597257⟩
- Ellen Gregory, Shilpi Kalra, Trisha Brock, Gisèle Bonne, G.W. Gant Luxton, et al.. Caenorhabditis elegans models for striated muscle disorders caused by missense variants of human LMNA. PLoS Genetics, 2023, 19 (8), pp.e1010895. ⟨10.1371/journal.pgen.1010895⟩. ⟨hal-04066711⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Julia Madsen-Østerbye, Mohamed Abdelhalim, Kamel Mamchaoui, Jessica Ohana, et al.. Cellular and Genomic Features of Muscle Differentiation from Isogenic Fibroblasts and Myoblasts. Cells, 2023, 12 (15), pp.1995. ⟨10.3390/cells12151995⟩. ⟨hal-04187751⟩
- Édouard Berling, Camille Verebi, Nadia Venturelli, Stéphane Vassilopoulos, Anthony Béhin, et al.. Caveolinopathy: Clinical, histological, and muscle imaging features and follow-up in a multicenter retrospective cohort. European Journal of Neurology, 2023, 30 (8), p.2506-2517. ⟨10.1111/ene.15832⟩. ⟨hal-04190879⟩
- Luce Barbat Du Closel, Nathalie Bonello-Palot, Yann Péréon, Andoni Echaniz-Laguna, Jean Philippe Camdessanche, et al.. Clinical and electrophysiological characteristics of women with X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. European Journal of Neurology, 2023, 30 (10), pp.3265-3276. ⟨10.1111/ene.15937⟩. ⟨hal-04254200⟩
- Laurane Mackels, Xincheng Liu, Gisèle Bonne, Laurent Servais. TOR1AIP1-Associated Nuclear Envelopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24, ⟨10.3390/ijms24086911⟩. ⟨hal-04066690⟩
- Lorenzo Maggi, Susana Quijano-Roy, Carsten Bönnemann, Gisèle Bonne. 253rd ENMC international workshop: Striated muscle laminopathies - natural history and clinical trial readiness. 24-26 June 2022, Hoofddorp, The Netherlands. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2023, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.04.009⟩. ⟨hal-04086238⟩
- Jean-Baptiste Chanson, Aleksandra Nadaj-Pakleza, Anne-Laure Bedat-Millet, Ariane Choumert, Anne Barnier, et al.. SORD-related peripheral neuropathy in a French and Swiss cohort: Clinical features, genetic analyses, and sorbitol dosages. European Journal of Neurology, 2023, 30 (7), pp.2001-2011. ⟨10.1111/ene.15793⟩. ⟨hal-04254194⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2023 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2023, 33 (1), pp.76-117. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2022.12.002⟩. ⟨hal-03964998⟩
- Tanya Stojkovic, Marion Masingue, Helène Turmel, Marianne Hezode-Arzel, Anthony Béhin, et al.. Diagnostic yield of a practical electrodiagnostic protocol discriminating between different congenital myasthenic syndromes. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2022, 32 (11-12), pp.870-878. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2022.10.001⟩. ⟨hal-04074000⟩
- Clémence Labasse, Guy Brochier, Ana-Lia Taratuto, Bruno Cadot, John Rendu, et al.. Severe ACTA1-related nemaline myopathy: intranuclear rods, cytoplasmic bodies, and enlarged perinuclear space as characteristic pathological features on muscle biopsies. Acta Neuropathologica Communications, 2022, 10 (1), pp.101. ⟨10.1186/s40478-022-01400-0⟩. ⟨hal-03820052⟩
- Tanya Stojkovic, Marion Masingue, Corinne Métay, Norma Romero, Bruno Eymard, et al.. LAMA2-Related Muscular Dystrophy: The Importance of Accurate Phenotyping and Brain Imaging in the Diagnosis of LGMD. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2022, pp.1-9. ⟨10.3233/JND-221555⟩. ⟨hal-03860537⟩
- Maude Vecten, Emmanuelle Pion, Marc Bartoli, Raul Juntas Morales, Damien Sternberg, et al.. Objective Evaluation of Clinical Actionability for Genes Involved in Myopathies: 63 Genes with a Medical Value for Patient Care. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23 (15), pp.8506. ⟨10.3390/ijms23158506⟩. ⟨hal-03751530⟩
- Helena Mosbah, Bruno Donadille, Camille Vatier, Sonja Janmaat, Michael Atlan, et al.. Dunnigan lipodystrophy syndrome: French National Diagnosis and Care Protocol (PNDS; Protocole National de Diagnostic et de Soins). Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2022, ⟨10.1186/s13023-022-02308-7⟩. ⟨hal-03649738⟩
- Hong Joo Kim, Payam Mohassel, Sandra Donkervoort, Lin Guo, Kevin O’donovan, et al.. Heterozygous frameshift variants in HNRNPA2B1 cause early-onset oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Nature Communications, 2022, 13 (1), pp.2306. ⟨10.1038/s41467-022-30015-1⟩. ⟨hal-03978696⟩
- Laura Le Gall, William J Duddy, Cecile Martinat, Virginie Mariot, Owen Connolly, et al.. Muscle cells of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients secrete neurotoxic vesicles. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle, 2022, 13 (2), pp.1385 - 1402. ⟨10.1002/jcsm.12945⟩. ⟨hal-04767184⟩
- Susana Quijano-Roy, Jana Haberlova, Claudia Castiglioni, John Vissing, Francina Munell, et al.. Diagnostic interest of whole-body MRI in early- and late-onset LAMA2 muscular dystrophies: a large international cohort. Journal of Neurology, 2022, 269, pp.2414-2429. ⟨10.1007/s00415-021-10806-0⟩. ⟨hal-03359688⟩
- Elke de Boer, Burcu Yaldiz, Anne-Sophie Denommé-Pichon, Leslie Matalonga, Steve Laurie, et al.. Genome-wide variant calling in reanalysis of exome sequencing data uncovered a pathogenic TUBB3 variant. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 2022, 65 (1), pp.104402. ⟨10.1016/j.ejmg.2021.104402⟩. ⟨hal-03864543⟩
- Abdallah Fayssoil, Lee S Nguyen, Tanya Stojkovic, Helene Prigent, Robert Carlier, et al.. Determinants of diaphragm inspiratory motion, diaphragm thickening, and its performance for predicting respiratory restrictive pattern in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle & Nerve, 2022, 65 (1), pp.89-95. ⟨10.1002/mus.27432⟩. ⟨hal-03521139⟩
- Konstantinos Savvatis, Christoffer Rasmus Vissing, Lori Klouvi, Anca Rezeda Florian, Mehjabin Rahman, et al.. Cardiac Outcomes in Adults With Mitochondrial Diseases. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2022, 80 (15), pp.1421-1430. ⟨10.1016/j.jacc.2022.08.716⟩. ⟨hal-03837169⟩
- Delphine Trochet, Bernard Prudhon, Lylia Mekzine, Mégane Lemaitre, Maud Beuvin, et al.. Benefits of therapy by dynamin-2-mutant-specific silencing are maintained with time in a mouse model of dominant centronuclear myopathy. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 2022, 27, pp.1179-1190. ⟨10.1016/j.omtn.2022.02.009⟩. ⟨hal-03659054⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Charles van Goethem, Corinne Thèze, Jacques Puechberty, Thomas Guignard, et al.. Long-Reads Sequencing Strategy to Localize Variants in TTN Repeated Domains. Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, In press, ⟨10.1016/j.jmoldx.2022.04.006⟩. ⟨hal-03672757⟩
- Maude Vecten, Emmanuelle Pion, Raul Juntas Morales, Damien Sternberg, John Rendu, et al.. Objective evaluation of clinical actionnability for genes involved in myopathies: 51 promising genes. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2022, European Joural of Human Genetics, 30 (SUPPL 1, 1), pp.306. ⟨hal-03678838⟩
- Silvia Torelli, Domenic Scaglioni, Valentina Sardone, Matthew J Ellis, Joana Domingos, et al.. High-Throughput Digital Image Analysis Reveals Distinct Patterns of Dystrophin Expression in Dystrophinopathy Patients. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 2021, 80 (10), pp.955 - 965. ⟨10.1093/jnen/nlab088⟩. ⟨hal-03454233⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou. MLIP: a novel gene causing rhabdomyolysis. Médecine/Sciences, 2021, 37, pp.48-48. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2021193⟩. ⟨hal-04009560⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou. MLIP : un nouveau gène de rhabdomyolyse. Médecine/Sciences, 2021, 37, pp.48-48. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2021193⟩. ⟨hal-03475162⟩
- Louise Benarroch. À la recherche de facteurs génétiques modificateurs dans les cardiomyopathies. Médecine/Sciences, 2021, 37, pp.49-49. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2021195⟩. ⟨hal-03842194⟩
- Lucie Isoline Pisella, Sara Fernandes, Guilhem Sole, Tanya Stojkovic, Celine Tard, et al.. A multicenter cross-sectional French study of the impact of COVID-19 on neuromuscular diseases. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2021, 16 (1), pp.450. ⟨10.1186/s13023-021-02090-y⟩. ⟨hal-03470914⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Enzo Cohen, Antonio Atalaia, Rabah Ben Yaou, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Preclinical Advances of Therapies for Laminopathies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2021, 10 (21), pp.4834. ⟨10.3390/jcm10214834⟩. ⟨hal-03430955⟩
- Rocío Villar-Quiles, Sandra Donkevoort, Alix de Becdelievre, Corine Gartioux, Valérie Jobic, et al.. Clinical and Molecular Spectrum Associated with COL6A3 c.7447A>G p.(Lys2483Glu) Variant: Elucidating its Role in Collagen VI-related Myopathies. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2021, 8 (4), pp.633-645. ⟨10.3233/JND-200577⟩. ⟨hal-03244986⟩
- Menelaos Pipis, Andrea Cortese, James M Polke, Roy Poh, Jana Vandrovcova, et al.. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2CC due to NEFH variants causes a progressive, non-length-dependent, motor-predominant phenotype. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 2021, jnnp-2021-327186. ⟨10.1136/jnnp-2021-327186⟩. ⟨hal-03353031⟩
- Rebecca Schüle, Dagmar Timmann, Corrie Erasmus, Jennifer Reichbauer, Melanie Wayand, et al.. Solving unsolved rare neurological diseases—a Solve-RD viewpoint. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, 29 (9), pp.1332-1336. ⟨10.1038/s41431-021-00901-1⟩. ⟨hal-03983726⟩
- Malika Foy, Philippe de Mazancourt, Corinne Métay, Robert Carlier, Valérie Allamand, et al.. A novel COL1A1 variant in a family with clinical features of hypermobile Ehlers‐Danlos syndrome that proved to be a COL1 ‐related overlap disorder. Clinical Case Reports, 2021, 9 (9), ⟨10.1002/ccr3.4128⟩. ⟨hal-04008076⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Raul Juntas Morales, Françoise Chapon, Corinne Thèze, Delphine Lacourt, et al.. Novel dominant distal titinopathy phenotype associated with copy number variation. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, In press, 8 (9), pp.1906-1912. ⟨10.1002/acn3.51434⟩. ⟨hal-03304664⟩
- Malika Foy, Philippe de Mazancourt, Corinne Métay, Robert Carlier, Valérie Allamand, et al.. A novel COL1A1 variant in a family with clinical features of hypermobile Ehlers‐Danlos syndrome that proved to be a COL1 ‐related overlap disorder. Clinical Case Reports, 2021, 9 (9), ⟨10.1002/ccr3.4128⟩. ⟨hal-04074072⟩
- Nicolas Vignier, Maria Chatzifrangkeskou, Luca Pinton, Hugo Wioland, Thibaut Marais, et al.. The non-muscle ADF/cofilin-1 controls sarcomeric actin filament integrity and force production in striated muscle laminopathies. Cell Reports, 2021, 36 (8), pp.109601. ⟨10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109601⟩. ⟨hal-03350074⟩
- Elke de Boer, Charlotte W. Ockeloen, Leslie Matalonga, Rita Horvath, Enzo Cohen, et al.. Correction: A MT-TL1 variant identified by whole exome sequencing in an individual with intellectual disability, epilepsy, and spastic tetraparesis (European Journal of Human Genetics, (2021), 29, 9, (1359-1368), 10.1038/s41431-021-00900-2). European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, 29 (9), pp.1470-1471. ⟨10.1038/s41431-021-00937-3⟩. ⟨hal-03403537⟩
- Malika Foy, Philippe de Mazancourt, Corinne Métay, Robert Carlier, Valérie Allamand, et al.. A novel COL1A1 variant in a family with clinical features of hypermobile Ehlers‐Danlos syndrome that proved to be a COL1 ‐related overlap disorder. Clinical Case Reports, 2021, ⟨10.1002/ccr3.4128⟩. ⟨hal-03274483⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Pomi Yun, Adele D’amico, Muntoni Francesco, Carsten Bönnemann, et al.. International retrospective natural history study of LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy Short Title: LMNA-CMD natural history. Brain Communications, 2021, ⟨10.1093/braincomms/fcab075/6220465⟩. ⟨hal-03270153⟩
- Birte Zurek, Kornelia Ellwanger, Lisenka E L M Vissers, Rebecca Schüle, Matthis Synofzik, et al.. Solve-RD: systematic pan-European data sharing and collaborative analysis to solve rare diseases. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, ⟨10.1038/s41431-021-00859-0⟩. ⟨hal-03270971⟩
- Ana Töpf, Angela Pyle, Helen Griffin, Leslie Matalonga, Katherine Schon, et al.. Exome reanalysis and proteomic profiling identified TRIP4 as a novel cause of cerebellar hypoplasia and spinal muscular atrophy (PCH1). European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, 29 (9), pp.1348 - 1353. ⟨10.1038/s41431-021-00851-8⟩. ⟨hal-03352467⟩
- Nguyen Thi Huong, Rocio-Nur Villar-Quiles, Van Thuy Le, Sarah Leonard-Louis, Lilia Laddada, et al.. Leukoencephalopathy and conduction blocks in PLEKHG5-associated intermediate CMT disease. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2021, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2021.06.004⟩. ⟨hal-03285057⟩
- Anna Katharina Sommer, Iris Te Paske, Farid Yavari Dizjikan, Chiara Marini Bettolo, Ivo Glynne Gut, et al.. Solving patients with rare diseases through programmatic reanalysis of genome-phenome data. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, 29 (9), pp.1337 - 1347. ⟨10.1038/s41431-021-00852-7⟩. ⟨hal-03352530v2⟩
- Sandra Coppens, Alison Barnard, Sanna Puusepp, Sander Pajusalu, Katrin Õunap, et al.. A form of muscular dystrophy associated with pathogenic variants in JAG2. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2021, 108 (6), pp.1164. ⟨10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.018⟩. ⟨hal-03854149⟩
- Raphaël Porcher, Isabelle Desguerre, Helge Amthor, Brigitte Chabrol, Frédérique Audic, et al.. Association between prophylactic angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and overall survival in Duchenne muscular dystrophy—analysis of registry data. European Heart Journal, 2021, ⟨10.1093/eurheartj/ehab054⟩. ⟨hal-03179750⟩
- Caroline Stalens, Leslie Motté, Anthony Béhin, Rabah Ben Yaou, France Leturcq, et al.. Improved cardiac outcomes by early treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in Becker muscular dystrophy. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2021, 8 (4), pp.495 - 502. ⟨10.3233/jnd-200620⟩. ⟨hal-03464423⟩
- Antonio Atalaia, Rabah Ben Yaou, Karim Wahbi, Annachiara de Sandre-Giovannoli, Corinne Vigouroux, et al.. Laminopathies’ Treatments Systematic Review: A Contribution Towards a ‘Treatabolome’. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2021, pp.1 - 21. ⟨10.3233/jnd-200596⟩. ⟨hal-03171665⟩
- Anne-Claire Guenantin, Imen Jebeniani, Julia Leschik, Erwan Watrin, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Targeting the histone demethylase LSD1 prevents cardiomyopathy in a mouse model of laminopathy. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2021, 131 (1), ⟨10.1172/JCI136488⟩. ⟨hal-03134235⟩
- Sandy Elbitar, Marjolijn Renard, Pauline Arnaud, Nadine Hanna, Marie-Paule Jacob, et al.. Pathogenic variants in THSD4, encoding the ADAMTS-like 6 protein, predispose to inherited thoracic aortic aneurysm. Genetics in Medicine, 2021, 23 (1), pp.111-122. ⟨10.1038/s41436-020-00947-4⟩. ⟨hal-03842198⟩
- Yvan de Feraudy, Rabah Ben Yaou, Karim Wahbi, Caroline Stalens, Amalia Stantzou, et al.. Very Low Residual Dystrophin Quantity Is Associated with Milder Dystrophinopathy. Annals of Neurology, 2021, 89 (2), pp.280-292. ⟨10.1002/ana.25951⟩. ⟨hal-03141478⟩
- Denisa Hathazi, Daniel Cox, Adele d'Amico, Giorgio Tasca, Richard Charlton, et al.. INPP5K and SIL1 associated pathologies with overlapping clinical phenotypes converge through dysregulation of PHGDH. Brain - A Journal of Neurology , 2021, 144 (8), pp.2427-2442. ⟨10.1093/brain/awab133⟩. ⟨hal-03401813⟩
- Giorgia Querin, Timothée Timothée Lenglet, Rabab Debs, Tanya Stojkovic, Anthony Behin, et al.. Development of new outcome measures for adult SMA type III and IV: a multimodal longitudinal study. Journal of Neurology, 2021, 268 (5), pp.1792-1802. ⟨10.1007/s00415-020-10332-5⟩. ⟨hal-03230903⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2022 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2021, 31 (12), pp.1313-1357. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2021.11.004⟩. ⟨hal-03498774⟩
- Daniel J Owens, Julien Messéant, Sophie Moog, Mark Viggars, Arnaud Ferry, et al.. Lamin-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy Alters Mechanical Signaling and Skeletal Muscle Growth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 22 (1), pp.306. ⟨10.3390/ijms22010306⟩. ⟨hal-03146374⟩
- Sergey N Bardakov, Roman V Deev, Raisat M Magomedova, Zoya R Umakhanova, Valérie Allamand, et al.. Intrafamilial Phenotypic Variability of Collagen VI-Related Myopathy Due to a New Mutation in the COL6A1 Gene. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2020, pp.1-12. ⟨10.3233/JND-200476⟩. ⟨hal-03094479⟩
- Sandra Donkervoort, Carl Kutzner, Ying Hu, Xavière Lornage, John Rendu, et al.. Pathogenic Variants in the Myosin Chaperone UNC-45B Cause Progressive Myopathy with Eccentric Cores. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2020, 107 (6), pp.1078-1095. ⟨10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.11.002⟩. ⟨hal-03668017⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2021 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2020, 30 (12), pp.1008-1048. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2020.11.009⟩. ⟨hal-03144209⟩
- Emmanuelle Campana-Salort, Gisèle Bonne, Valérie Allamand, J. Andoni Urtizberea. 2020, une année entre parenthèses. Médecine/Sciences, 2020, 36, pp.5 - 5. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2020268⟩. ⟨hal-03270951⟩
- Louis M Viollet, Kathryn J Swoboda, Rong Mao, Hunter Best, Youna Ha, et al.. A novel pathogenic variant in DYNC1H1 causes various upper and lower motor neuron anomalies. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 2020, 63 (12), pp.104063. ⟨10.1016/j.ejmg.2020.104063⟩. ⟨hal-03182670⟩
- Valérie Allamand. L’intérêt d’inclure l’analyse SMA dans les panels NGS de maladies neuromusculaires. Médecine/Sciences, 2020, 36, pp.51-52. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2020209⟩. ⟨hal-03838506⟩
- Antonio Atalaia, Rachel Thompson, Alberto Corvo, Leigh Carmody, Davide Piscia, et al.. A guide to writing systematic reviews of rare disease treatments to generate FAIR-compliant datasets: building a Treatabolome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2020, 15 (1), pp.206. ⟨10.1186/s13023-020-01493-7⟩. ⟨hal-02935405⟩
- Hannah Nicolas, Anne T Bertrand, Sarah Labib, Musfira Mohamed-Uvaize, Pierrette Bolongo, et al.. Protein Kinase C Alpha Cellular Distribution, Activity, and Proximity with Lamin A/C in Striated Muscle Laminopathies. Cells, 2020, 9 (11), pp.2388. ⟨10.3390/cells9112388⟩. ⟨hal-03169708⟩
- Matthew Jennings, Angela Lochmüller, Antonio Atalaia, Rita Horvath. Targeted Therapies for Hereditary Peripheral Neuropathies: Systematic Review and Steps Towards a ‘treatabolome’. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2020, pp.1-18. ⟨10.3233/JND-200546⟩. ⟨hal-03144329⟩
- Blanca Morales Rodriguez, Alejandro Domínguez-Rodríguez, Jean-Pierre Benitah, Florence Lefebvre, Thibaut Marais, et al.. Activation of sarcolipin expression and altered calcium cycling in LMNA cardiomyopathy. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2020, 22, pp.100767. ⟨10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100767⟩. ⟨hal-03269952⟩
- Thomas Grange, Mélodie Aubart, Maud Langeois, Louise Benarroch, Pauline Arnaud, et al.. Quantifying the Genetic Basis of Marfan Syndrome Clinical Variability. Genes, 2020, 11 (5), pp.574. ⟨10.3390/genes11050574⟩. ⟨hal-03842208⟩
- Déborah Gómez-Domínguez, Carolina Epifano, Fernando De Miguel, Albert García Castaño, Borja Vilaplana-Martí, et al.. Consequences of Lmna Exon 4 Mutations in Myoblast Function. Cells, 2020, 9 (5), pp.1286. ⟨10.3390/cells9051286⟩. ⟨hal-03153669⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Corinne Metay, Marcello Villanova, Robert-Yves Carlier, Elena Pegoraro, et al.. A new congenital multicore titinopathy associated with fast myosin heavy chain deficiency. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, 2020, ⟨10.1002/acn3.51031⟩. ⟨hal-02573441⟩
- Ashley Earle, Tyler Kirby, Gregory Fedorchak, Philipp Isermann, Jineet Patel, et al.. Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells. Nature Materials, 2020, 19 (4), pp.464-473. ⟨10.1038/s41563-019-0563-5⟩. ⟨hal-03855903⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Louise Benarroch, Khadija Chikhaoui, et al.. Lamin A/C Assembly Defects in LMNA-Congenital Muscular Dystrophy Is Responsible for the Increased Severity of the Disease Compared with Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. Cells, 2020, ⟨10.3390/cells9040844⟩. ⟨hal-02527633⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Satoru Noguchi, Shinichiro Hayashi, Harumasa Nakamura, Hirofumi Komaki, et al.. Exon skipping induced by nonsense/frameshift mutations in DMD gene results in Becker muscular dystrophy. Human Genetics, 2020, 139 (2), pp.247-255. ⟨10.1007/s00439-019-02107-4⟩. ⟨hal-03842189⟩
- A. Reghan Foley, Yaqun Zou, James E. Dunford, Jachinta Rooney, Goutam Chandra, et al.. GGPS1 Mutations Cause Muscular Dystrophy/Hearing Loss/Ovarian Insufficiency Syndrome. Annals of Neurology, 2020, 88 (2), pp.332-347. ⟨10.1002/ana.25772⟩. ⟨hal-02938442⟩
- Guillermo Tarrasó, Alberto Real-Martinez, Marta Parés, Lídia Romero-Cortadellas, Laura Puigros, et al.. Absence of p.R50X Pygm read-through in McArdle disease cellular models. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 2020, 13 (1), pp.dmm043281. ⟨10.1242/dmm.043281⟩. ⟨hal-02492150⟩
- Laurent Meertens, Mohamed Lamine Hafirassou, Thérèse Couderc, Lucie Bonnet-Madin, Vasiliya Kril, et al.. FHL1 is a key player of chikungunya virus tropism and pathogenesis. Comptes Rendus. Biologies, 2020, 343 (4), pp.79-89. ⟨10.5802/crbiol.40⟩. ⟨pasteur-03246117⟩
- Malek Kammoun, Jérôme Piquereau, Vladimir Veksler, Lydie Nadal-Desbarats, Sandra Même, et al.. Novel Role of Tieg1 in Muscle Metabolism and Mitochondrial Oxidative Capacities. Acta Physiologica, 2020, 228 (3), pp.e13394. ⟨10.1111/apha.13394⟩. ⟨hal-02304067v2⟩
- Vahid M. Harandi, Bernardo Moreira Soares Oliveira, Valérie Allamand, Ariana Friberg, Cibely C Fontes-Oliveira, et al.. Antioxidants Reduce Muscular Dystrophy in the dy2J/dy2J Mouse Model of Laminin α2 Chain-Deficient Muscular Dystrophy. Antioxidants , 2020, 9 (3), pp.244. ⟨10.3390/antiox9030244⟩. ⟨hal-02552023⟩
- Katarzyna Piekarowicz, Anne T Bertrand, Feriel Azibani, Maud Beuvin, Laura Julien, et al.. A muscle hybrid promoter as a novel tool for gene therapy. Molecular Therapy - Methods and Clinical Development, 2019, 15 (8), pp.157 - 169. ⟨10.1016/j.omtm.2019.09.001⟩. ⟨hal-03269927⟩
- Tsui Han Loo, Xiaoqian Ye, Ruth Jinfen Chai, Mitsuteru Ito, Gisele Bonne, et al.. The mammalian LINC complex component SUN1 regulates muscle regeneration by modulating drosha activity. eLife, 2019, 8, ⟨10.7554/eLife.49485⟩. ⟨hal-02573415⟩
- Valérie Allamand. Génétique : Une mutation du gène TNPO3 impliquée dans la LGMD D2 confère une protection à l’infection par le VIH-1. Médecine/Sciences, 2019, 35, pp.45-46. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2019240⟩. ⟨hal-03838210⟩
- Leroy Joseph, Uma Mahesh R. Avula, Elaine Wan, Michael Reyes, Kundanika Lakkadi, et al.. Dietary Saturated Fat Promotes Arrhythmia by Activating NOX2 (NADPH Oxidase 2). Circulation. Arrhythmia and electrophysiology, 2019, 12 (11), ⟨10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007573⟩. ⟨hal-03859478⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2020 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2019, 29 (12), pp.980-1018. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.10.010⟩. ⟨hal-02393145⟩
- E. Gargaun, K. Wahbi, R. Ben Yaou, M. Guibaud, G. Solé, et al.. Phenotypic and genomic characterization as predictors of DMD 45 to 55 multi-exon skipping therapy. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2019, 29, pp.S165. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.449⟩. ⟨cea-04414398⟩
- Nicolas Vignier, Nathalie Mougenot, Gisèle Bonne, Antoine Muchir. Effect of genetic background on the cardiac phenotype in a mouse model of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2019, 19, pp.100664. ⟨10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100664⟩. ⟨hal-03464625⟩
- Marion Brisset, Rabah Ben Yaou, Robert-Yves Carlier, Anaїs Chanut, Guillaume Nicolas, et al.. X-linked Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy manifesting with adult onset axial weakness, camptocormia, and minimal joint contractures. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2019, 29 (9), pp.678-683. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.009⟩. ⟨hal-03864398⟩
- Eiji Wada, Megumi Kato, Kaori Yamashita, Hiroko Kokuba, Wen-Chen Liang, et al.. Deficiency of emerin contributes differently to the pathogenesis of skeletal and cardiac muscles in LmnaH222P/H222P mutant mice. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14 (8), pp.e0221512. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0221512⟩. ⟨inserm-02271145⟩
- Alan H. Beggs, Gisèle Bonne, Carsten Bönnemann, Sandra Donkervoort, James J. Dowling, et al.. 214th ENMC International Workshop: Establishing an international consortium for gene discovery and clinical research for Congenital Muscle Disease, Heemskerk, the Netherlands, 6–18 October 2015. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2019, 29 (8), pp.644-650. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.07.002⟩. ⟨hal-02388590⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, France Leturcq, Rabah Ben Yaou. Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. Gene Reviews, 2019. ⟨hal-03292021⟩
- Karim Wahbi, Rabah Ben Yaou, Estelle Gandjbakhch, Frédéric Anselme, Thomas Gossios, et al.. Development and Validation of a New Risk Prediction Score for Life-Threatening Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias in Laminopathies. Circulation, 2019, 140 (4), pp.293-302. ⟨10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.039410⟩. ⟨hal-02237297⟩
- M de Antonio, C Dogan, B Eymard, J Puymirat, J Mathieu, et al.. The DM-scope registry: a rare disease innovative framework bridging the gap between research and medical care. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2019. ⟨hal-04015406⟩
- Rachel Thompson, Gisèle Bonne, Paolo Missier, Hanns Lochmuller. Targeted therapies for congenital myasthenic syndromes: systematic review and steps towards a treatabolome. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2019, 3 (1), pp.19-37. ⟨10.1042/ETLS20180100⟩. ⟨hal-02413203⟩
- Véronique Bolduc, A. Reghan Reghan Foley, Herimela Solomon-Degefa, Apurva Sarathy, Sandra Donkervoort, et al.. A recurrent COL6A1 pseudoexon insertion causes muscular dystrophy and is effectively targeted by splice-correction therapies. JCI Insight, 2019, 4 (6), ⟨10.1172/jci.insight.124403⟩. ⟨hal-03285227⟩
- Nadine Ame van der Beek, Isabelle Nelson, Roseline Froissart, Thierry Levade, Virginie Garcia, et al.. A new case of SMA phenotype without epilepsy due to biallelic variants in ASAH1. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2019, 27 (3), pp.337-339. ⟨10.1038/s41431-018-0250-z⟩. ⟨hal-03855754⟩
- Willem de Ridder, Isabelle Nelson, Bob Asselbergh, Boel de Paepe, Maud Beuvin, et al.. Muscular dystrophy with arrhythmia caused by loss-of-function mutations in BVES. Neurology Genetics, 2019, 5 (2), pp.e321. ⟨10.1212/NXG.0000000000000321⟩. ⟨hal-03855787⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Mélodie Aubart, Marie-Sylvie Gross, Pauline Arnaud, Nadine Hanna, et al.. Reference Expression Profile of Three FBN1 Transcript Isoforms and Their Association with Clinical Variability in Marfan Syndrome. Genes, 2019, 10 (2), pp.128. ⟨10.3390/genes10020128⟩. ⟨hal-03842211⟩
- Matteo Garibaldi, John Rendu, Julie Brocard, Emmanuelle Lacène, Julien Fauré, et al.. ‘Dusty core disease’ (DuCD): expanding morphological spectrum of RYR1 recessive myopathies. Acta Neuropathologica Communications, 2019, 7 (3), ⟨10.1186/s40478-018-0655-5⟩. ⟨hal-01973947⟩
- Johanna Palmio, Sarah Léonard-Louis, Sabrina Sacconi, Marco Savarese, Sini Penttilä, et al.. Expanding the importance of HMERF titinopathy: new mutations and clinical aspects. Journal of Neurology, 2019, 266 (3), pp.680-690. ⟨10.1007/s00415-019-09187-2⟩. ⟨hal-02064991⟩
- Alberto Real-Martinez, Astrid Brull, Jordi Huerta, Guillermo Tarrasó, Alejandro Lucia, et al.. Low survival rate and muscle fiber-dependent aging effects in the McArdle disease mouse model. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, pp.5116. ⟨10.1038/s41598-019-41414-8⟩. ⟨hal-02094633⟩
- Rainiero Ávila-Polo, Edoardo Malfatti, Xavière Lornage, Chrystel Cheraud, Isabelle Nelson, et al.. Loss of Sarcomeric Scaffolding as a Common Baseline Histopathologic Lesion in Titin-Related Myopathies. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 2018, 77 (12), pp.1101-1114. ⟨10.1093/jnen/nly095⟩. ⟨hal-02332968⟩
- David Gómez-Andrés, Jordi Diaz-Manera, Aida Alejaldre, Irene Pulido-Valdeolivas, Laura González-Mera, et al.. Muscle imaging in laminopathies: Synthesis study identifies meaningful muscles for follow-up. Muscle & nerve. Supplement., 2018, 58 (6), pp.812-817. ⟨10.1002/mus.26312⟩. ⟨hal-02297512⟩
- Laura Castellani, Jennifer Wilkin, Andrew Abela, Louise Benarroch, Zohra Ahasan, et al.. Effects of acute olanzapine exposure on central insulin-mediated regulation of whole body fuel selection and feeding. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2018, 98, pp.127-130. ⟨10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.07.028⟩. ⟨hal-03842226⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Jean Pouget. L’errance diagnostique au cœur des préoccupations du 3 e Plan National Maladies Rares. Médecine/Sciences, 2018, 34, pp.5-5. ⟨10.1051/medsci/201834s201⟩. ⟨hal-03855810⟩
- Astrid Brull, Blanca Morales Rodriguez, Gisele Bonne, Antoine Muchir, Anne T Bertrand. The Pathogenesis and Therapies of Striated Muscle Laminopathies. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9, pp.1533. ⟨10.3389/fphys.2018.01533⟩. ⟨hal-01919521⟩
- Maxime Kwapich, Dominique Lacroix, Stéphanie Espiard, Sandro Ninni, François Brigadeau, et al.. Cardiometabolic assessment of lamin A/C gene mutation carriers: A phenotype-genotype correlation.. Diabetes & Metabolism, 2018, Diabetes & metabolism, 45, pp.382-389. ⟨10.1016/j.diabet.2018.09.006⟩. ⟨hal-02368608⟩
- Maria Chatzifrangkeskou, David Yadin, Thibaut Marais, Solenne Chardonnet, Mathilde Cohen-Tannoudji, et al.. Cofilin-1 phosphorylation catalyzed by ERK1/2 alters cardiac actin dynamics in dilated cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutation. Human Molecular Genetics, 2018, 27 (17), pp.3060-3078. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddy215⟩. ⟨hal-01962065⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2019 version of the gene table of neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2018, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2018.09.006⟩. ⟨hal-01934859⟩
- Matthieu Le Dinh, Serge Carreira, Julie Obert, Ghislaine Gayan-Ramirez, Bruno Riou, et al.. Prolonged mechanical ventilation worsens sepsis-induced diaphragmatic dysfunction in the rat. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13 (8), pp.e0200429. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0200429⟩. ⟨inserm-02426442⟩
- Abdallah Fayssoil, Lee Nguyen, Adam Ogna, Paris Meng, Olivier Nardi, et al.. Effects of Home Mechanical Ventilation on Left Ventricular Function in Sarcoglycanopathies (Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies). American Journal of Cardiology, 2018, 122 (2), pp.353-355. ⟨10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.04.001⟩. ⟨inserm-04015389⟩
- Eleonora Cavallari, Carla Carrera, Matteo Sorge, Gisèle Bonne, Antoine Muchir, et al.. The 13C hyperpolarized pyruvate generated by ParaHydrogen detects the response of the heart to altered metabolism in real time. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8 (1), ⟨10.1038/s41598-018-26583-2⟩. ⟨hal-03270932⟩
- Leandro Ladislau, Débora M. Portilho, Tristan Courau, Alhondra Solares-Pérez, Elisa Negroni, et al.. Activated dendritic cells modulate proliferation and differentiation of human myoblasts. Cell Death and Disease, 2018, 9 (5), pp.551. ⟨10.1038/s41419-018-0426-z⟩. ⟨hal-03273530v2⟩
- P. H. Jonson, J. Palmio, M. Johari, S. Penttilä, A. Evilä, et al.. Novel mutations in DNAJB6 cause LGMD1D and distal myopathy in French families. European Journal of Neurology, 2018, 25 (5), pp.790-794. ⟨10.1111/ene.13598⟩. ⟨hal-02304997⟩
- Sofie Thurø Østergaard, Katherine Johnson, Tanya Stojkovic, Thomas Krag, Willem de Ridder, et al.. Limb girdle muscular dystrophy due to mutations in POMT2. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 2018, 89 (5), pp.506-512. ⟨10.1136/jnnp-2017-317018⟩. ⟨hal-03864445⟩
- Alexandre Janin, Delphine Bauer, Francesca Ratti, Camille Valla, Anne T Bertrand, et al.. SMAD6 overexpression leads to accelerated myogenic differentiation of LMNA mutated cells. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8 (1), ⟨10.1038/s41598-018-23918-x⟩. ⟨hal-03270318⟩
- Feriel Azibani, Astrid Brull, Ludovic Arandel, Maud Beuvin, Isabelle Nelson, et al.. Gene Therapy via Trans-Splicing for LMNA-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 2018, 10, pp.376 - 386. ⟨10.1016/j.omtn.2017.12.012⟩. ⟨hal-03269960⟩
- Gabriella Captur, Eloisa Arbustini, Gisèle Bonne, Petros Syrris, Kevin Mills, et al.. Lamin and the heart. Heart, 2018, 104 (6), pp.468-479. ⟨10.1136/heartjnl-2017-312338⟩. ⟨hal-03285171⟩
- Abdallah Fayssoil, Rabah Ben Yaou, Adam Ogna, Cendrine Chaffaut, France Leturcq, et al.. Left bundle branch block in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Prevalence, genetic relationship and prognosis. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13 (1), pp.e0190518. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0190518⟩. ⟨hal-04015387⟩
- Blanca Morales Rodriguez, Lara Khouzami, Valérie Decostre, Shaida Varnous, Vanja Pekovic-Vaughan, et al.. N-acetyl cysteine alleviates oxidative stress and protects mice from dilated cardiomyopathy caused by mutations in nuclear A-type lamins gene. Human Molecular Genetics, 2018, 27 (19), pp.3353-3360. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddy243⟩. ⟨hal-01961216⟩
- Zoi Galata, Ismini Kloukina, Ioanna Kostavasili, Aimilia Varela, Constantinos H Davos, et al.. Amelioration of desmin network defects by αB-crystallin overexpression confers cardioprotection in a mouse model of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by LMNA gene mutation. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2018, 125, pp.73-86. ⟨10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.10.017⟩. ⟨hal-02292777⟩
- Nicolas Vignier, Maria Chatzifrangkeskou, Blanca Morales Rodriguez, Mathias Mericskay, Nathalie Mougenot, et al.. Rescue of biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide protects the heart in cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutation. Human Molecular Genetics, 2018, 27 (22), pp.3870-3880. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddy278⟩. ⟨hal-01958003⟩
- Coline Macquart, Rene Jüttner, Blanca Morales Rodriguez, Caroline Le Dour, Florence Lefebvre, et al.. Microtubule cytoskeleton regulates Connexin 43 localization and cardiac conduction in cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in A-type lamins gene. Human Molecular Genetics, 2018, 28 (24), pp.4043-4052. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddy227⟩. ⟨hal-02505679⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Philippe Latour, Vincent Procaccio, Claude Jardel, Mathieu Cerino, et al.. Vers une harmonisation du diagnostic par séquençage haut débit des maladies neuromusculaires. Médecine/Sciences, 2018, 34 (Hors-série 2), pp.20-22. ⟨10.1051/medsci/201834s206⟩. ⟨hal-01938567⟩
- Delphine Trochet, Bernard Prudhon, Maud Beuvin, Cécile Peccate, Stéphanie Lorain, et al.. Allele‐specific silencing therapy for Dynamin 2‐related dominant centronuclear myopathy. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2018, 10 (2), pp.239-253. ⟨10.15252/emmm.201707988⟩. ⟨hal-02000303⟩
- Pia Bernasconi, Nicola Carboni, Giulia Ricci, Gabriele Siciliano, Luisa Politano, et al.. Elevated TGF β2 serum levels in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy: Implications for myocyte and tenocyte differentiation and fibrogenic processes. Nucleus, 2018, 9 (1), pp.337-349. ⟨10.1080/19491034.2018.1467722⟩. ⟨hal-02297778⟩
- Marine Guilbaud, Christel Gentil, Cecile Peccate, Elena Gargaun, Isabelle Holtzmann, et al.. miR-708-5p and miR-34c-5p are involved in nNOS regulation in dystrophic context. Skeletal Muscle, 2018, 8 (1), pp.15. ⟨10.1186/s13395-018-0161-2⟩. ⟨hal-01792009⟩
- Candice Kutchukian, Peter Szentesi, Bruno Allard, Delphine Trochet, Maud Beuvin, et al.. Impaired excitation-contraction coupling in muscle fibres from the dynamin2 R465W mouse model of centronuclear myopathy. The Journal of Physiology, 2017, 595 (24), pp.7369-7382. ⟨10.1113/JP274990⟩. ⟨hal-03819840⟩
- Delphine Trochet, Bernard Prudhon, Maud Beuvin, Cécile Peccate, Stéphanie Lorain, et al.. Allele-specific silencing therapy for Dynamin 2-related dominant centronuclear myopathy. Circulation. Arrhythmia and electrophysiology, 2017, 10 (12), pp.428-431. ⟨10.15252/emmm.201707988⟩. ⟨hal-04001377⟩
- Céline Tard, Vincent Tiffreau, Emmanuelle Jaillette, Fabienne Jouen, Isabelle Nelson, et al.. Anti-HMGCR antibody–related necrotizing zutoimmune myopathy mimicking muscular dystrophy. Neuropediatrics, 2017, 48 (06), pp.473-476. ⟨10.1055/s-0037-1604402⟩. ⟨hal-03855669⟩
- Valérie Allamand. Muscle Membrane Serendipity conference : Past, Present, and Future Conference. Médecine/Sciences, 2017, 33, pp.67-67. ⟨10.1051/medsci/201733s116⟩. ⟨hal-03838486⟩
- Abdallah Fayssoil, Rabah Ben Yaou, Adam Ogna, France Leturcq, Olivier Nardi, et al.. Clinical profiles and prognosis of acute heart failure in adult patients with dystrophinopathies on home mechanical ventilation. ESC Heart Failure, 2017, 4 (4), pp.527-534. ⟨10.1002/ehf2.12165⟩. ⟨hal-04015409⟩
- Valérie Allamand. Génétique : Intérêt du NGS dans un cas atypique de LGMD liée à l’alphadystroglycane. Médecine/Sciences, 2017, 33, pp.57-57. ⟨10.1051/medsci/201733s112⟩. ⟨hal-03838503⟩
- Abdallah Fayssoil, Rabah Ben Yaou, Adam Ogna, France Leturcq, Olivier Nardi, et al.. Clinical profiles and prognosis of acute heart failure in adult patients with dystrophinopathies on home mechanical ventilation. ESC Heart Failure, 2017, 4 (4), pp.527-534. ⟨10.1002/ehf2.12165⟩. ⟨hal-04015397⟩
- V. Mariot, R. Joubert, C. Hourdé, L. Féasson, M. Hanna, et al.. Myostatin expression levels in neuromuscular diseases participates in anti-myostatin clinical failure. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2017, 27, pp.S231. ⟨10.1016/J.NMD.2017.06.490⟩. ⟨hal-03158311⟩
- Felice Heller, Ivana Dabaj, Jean Mah, Jean Bergounioux, Aben Essid, et al.. Cardiac manifestations of congenital LMNA-related muscular dystrophy in children: three case reports and recommendations for care. Cardiology in the Young, 2017, 27 (6), pp.1076-1082. ⟨10.1017/S1047951116002079⟩. ⟨hal-03860662⟩
- Christine Schwartz, Martina Fischer, Kamel Mamchaoui, Anne Bigot, Thevy Lok, et al.. Lamins and nesprin-1 mediate inside-out mechanical coupling in muscle cell precursors through FHOD1. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7 (1), pp.1253. ⟨10.1038/s41598-017-01324-z⟩. ⟨hal-01518113⟩
- Mark Pines, Oshrat Levi, Olga Genin, Adi Lavy, Corrado Angelini, et al.. Elevated Expression of Moesin in Muscular Dystrophies. American Journal of Pathology, 2017, 187 (3), pp.654-664. ⟨10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.11.013⟩. ⟨hal-03838202⟩
- Simon Guiraud, Tiffany Migeon, Arnaud Ferry, Zhiyong Chen, Souhila Ouchelouche, et al.. HANAC Col4a1 Mutation in Mice Leads to Skeletal Muscle Alterations due to a Primary Vascular Defect. American Journal of Pathology, 2017, 187 (3), pp.505-516. ⟨10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.10.020⟩. ⟨hal-03831011⟩
- Mathieu Cerino, Svetlana Gorokhova, Pascal Laforet, Rabah Ben Yaou, Emmanuelle Salort-Campana, et al.. Genetic Characterization of a French Cohort of GNE-mutation negative inclusion body myopathy patients with exome sequencing. Muscle & Nerve, 2017, 56, pp.993-997. ⟨10.1002/mus.25638⟩. ⟨hal-01741741⟩
- Audrey de Jong, Serge Carreira, Na Na, Aude Carillion, Cheng Jiang, et al.. Diaphragmatic function is enhanced in fatty and diabetic fatty rats. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12 (3), pp.e0174043. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0174043⟩. ⟨hal-01502168⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Aurelie Hubert, Isabelle Nelson, Julia R. Dahlqvist, David Gaist, et al.. Clinical heterogeneity and phenotype/genotype findings in 5 families with &ITGYG1&IT deficiency. Neurology Genetics, 2017, 3 (6), pp.e208. ⟨10.1212/NXG.0000000000000208⟩. ⟨hal-04010378v2⟩
- Stéphanie Bauché, Geoffroy Vellieux, Damien Sternberg, Marie-Joséphine Fontenille, Elodie de Bruyckere, et al.. Mutations in GFPT1-related congenital myasthenic syndromes are associated with synaptic morphological defects and underlie a tubular aggregate myopathy with synaptopathy. Journal of Neurology, 2017, 264 (8), pp.1791-1803. ⟨10.1007/s00415-017-8569-x⟩. ⟨hal-01653176⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Francois Rivier, Dalil Hamroun. The 2018 version of the gene table of monogenic neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular Disorders, 2017, 27 (12), pp.1152-1183. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.10.005⟩. ⟨hal-01668854⟩
- D. Avila-Smirnow, L. Gueneau, S. Batonnet-Pichon, F. Delort, H.-M. Bécane, et al.. Cardiac arrhythmia and late-onset muscle weakness caused by a myofibrillar myopathy with unusual histopathological features due to a novel missense mutation in FLNC. Revue Neurologique, 2016, 172 (10), pp.594-606. ⟨10.1016/j.neurol.2016.07.017⟩. ⟨hal-04021574⟩
- L. Davignon, C. Chauveau, C. Julien, C. Dill, L. Duband-Goulet, et al.. Loss-of-function mutation of TRIP4 causes a novel form of congenital muscle disease and reveals the transcription coactivator ASC-1 as a new regulator of skeletal myogenesis. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2016, 26 (suppl 2), pp.S118--S119. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2016.06.121⟩. ⟨hal-01415936⟩
- Stéphanie Bauché, Seana O’regan, Yoshiteru Azuma, Fanny Laffargue, Grace Mcmacken, et al.. Impaired Presynaptic High-Affinity Choline Transporter Causes a Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome with Episodic Apnea. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2016, 99 (3), pp.753 - 761. ⟨10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.06.033⟩. ⟨hal-01680226⟩
- Isabelle Marey, Rabah Ben Yaou, Nathalie Deburgrave, Aurélie Vasson, Juliette Nectoux, et al.. Non Random Distribution of DMD Deletion Breakpoints and Implication of Double Strand Breaks Repair and Replication Error Repair Mechanisms. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2016, 3 (2), pp.227 - 245. ⟨10.3233/JND-150134⟩. ⟨hal-01815023⟩
- Laurianne Davignon, Claire Chauveau, Cédric Julien, Corinne Dill, Isabelle Duband-Goulet, et al.. The transcription coactivator ASC-1 is a regulator of skeletal myogenesis, and its deficiency causes a novel form of congenital muscle disease. Human Molecular Genetics, 2016, 25 (8), pp.1559--1573. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddw033⟩. ⟨hal-01295646⟩
- M. Saunier, C.G. Bönnemann, M. Durbeej, V. Allamand. 212th ENMC International Workshop: Animal models of congenital muscular dystrophies, May 29th-31st, 2015 in Naarden, The Netherlands,. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2016, 26 (3), pp.252-259. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2016.02.002⟩. ⟨hal-01293003⟩
- Marie-Elodie Cattin, Arnaud Ferry, Alban Vignaud, Nathalie Mougenot, Adeline Jacquet, et al.. Mutation in lamin A/C sensitizes the myocardium to exercise-induced mechanical stress but has no effect on skeletal muscles in mouse. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2016, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2016.05.010⟩. ⟨hal-01329664⟩
- Elena Gargaun, Andreea Mihaela Seferian, Ruxandra Cardas, Anne-Gaelle Le Moing, Catherine Delanoe, et al.. EGR2 mutation enhances phenotype spectrum of Dejerine-Sottas syndrome. Journal of Neurology, 2016, 263 (7), pp.1456-1458. ⟨10.1007/s00415-016-8153-9⟩. ⟨hal-03604457⟩
- Rafael de Cid, Rabah Ben Yaou, Carinne Roudaut, Karine Charton, Sylvain Baulande, et al.. A new titinopathy. Neurology, 2015, 85 (24), pp.2126-2135. ⟨10.1212/WNL.0000000000002200⟩. ⟨hal-02336883⟩
- France Nelson, France Stojkovic, France Allamand, France Leturcq, Henri-Marc Becane, et al.. Laminin α2 Deficiency-Related Muscular Dystrophy Mimicking Emery-Dreifuss and Collagen VI related Diseases. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2015, 2 (3), pp.229 - 240. ⟨10.3233/JND-150093⟩. ⟨hal-01681760⟩
- Juliette Nectoux, Rafael de Cid, Sylvain Baulande, France Leturcq, Jon Andoni Urtizberea, et al.. Detection of TRIM32 deletions in LGMD patients analyzed by a combined strategy of CGH array and massively parallel sequencing. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2015, 23 (7), pp.929-934. ⟨10.1038/ejhg.2014.223⟩. ⟨hal-02190709⟩
- Aurélie Nicolas, Céline Raguénès-Nicol, Rabah Ben Yaou, Sarah Ameziane-Le Hir, Angélique Chéron, et al.. Becker muscular dystrophy severity is linked to the structure of dystrophin.. Human Molecular Genetics, 2015, 24 (5), pp.1267-79. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddu537⟩. ⟨hal-01117005⟩
- Florian Barthelemy, Claire L. Navarro, Racha Fayek, Nathalie da Silva, Patrice Roll, et al.. Truncated prelamin A expression in HGPS-like patients: a transcriptional study. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2015, 23 (8), pp.1051 - 1061. ⟨10.1038/ejhg.2014.239⟩. ⟨hal-01597886⟩
- Annachiara de Sandre-Giovannoli, Nicolas Lévy, Rabah Ben Yaou, France Leturcq, Giovanna Lattanzi, et al.. An overview of new translational, clinical and therapeutic perspectives in laminopathies and other nuclear envelope-related diseases.. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2015, 10 (Suppl 2), ⟨10.1186/1750-1172-10-S2-I1⟩. ⟨hal-01769449⟩
- Frédérique Rau, Jeanne Lainé, Laetitita Ramanoudjame, Arnaud Ferry, Ludovic Arandel, et al.. Abnormal splicing switch of DMD's penultimate exon compromises muscle fibre maintenance in myotonic dystrophy. Nature Communications, 2015, 6 (1), pp.7205. ⟨10.1038/ncomms8205⟩. ⟨hal-01162385⟩
- Laetitia Ramanoudjame, Claire Rocancourt, Jeanne Lainé, Arnaud Klein, Lucette Joassard, et al.. Two novel COLVI long chains in zebrafish that are essential for muscle development. Human Molecular Genetics, 2015, 24 (23), pp.6624-6639. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddv368⟩. ⟨hal-01594462⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Rabah Ben Yaou. A common French-Italian laminopathy registry – update & future prospects. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2015, 10 (Suppl 2), pp.O31. ⟨10.1186/1750-1172-10-S2-O31⟩. ⟨hal-01227847⟩
- Imen Dorboz, Marie Coutelier, Anne T. Bertrand, Jean-Hubert Caberg, Monique Elmaleh-Bergès, et al.. Severe dystonia, cerebellar atrophy, and cardiomyopathy likely caused by a missense mutation in TOR1AIP1. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2014, 9 (1), pp.174. ⟨10.1186/s13023-014-0174-9⟩. ⟨hal-01110718⟩
- Caroline Le Guiner, Marie Montus, Laurent Servais, Yan Cherel, Virginie François, et al.. Forelimb Treatment in a Large Cohort of Dystrophic Dogs Supports Delivery of a Recombinant AAV for Exon Skipping in Duchenne Patients. Molecular Therapy, 2014, 22 (11), pp.1923-1935. ⟨10.1038/mt.2014.151⟩. ⟨inserm-02447482⟩
- Anne Bertrand, Simindokht Ziaei, Camille Ehret, Hélène Duchemin, Kamel Mamchaoui, et al.. Cellular microenvironments reveal defective mechanosensing responses and elevated YAP signaling in LMNA-mutated muscle precursors. Journal of Cell Science, 2014, 127 (13), pp.2873-2884. ⟨10.1242/jcs.144907⟩. ⟨inserm-02426468⟩
- Stéphane Vassilopoulos, Christel Gentil, Jeanne Lainé, Pierre-Olivier Buclez, Agathe Franck, et al.. Actin scaffolding by clathrin heavy chain is required for skeletal muscle sarcomere organization. Journal of Cell Biology, 2014, 205 (3), pp.377-393. ⟨10.1083/jcb.201309096⟩. ⟨hal-02453865⟩
- Marie-Elodie Cattin, Anne T Bertrand, Saskia Schlossarek, Marie-Catherine Le Bihan, Søren Skov Jensen, et al.. Heterozygous LmnadelK32 mice develop dilated cardiomyopathy through a combined pathomechanism of haploinsufficiency and peptide toxicity.. Human Molecular Genetics, 2013, 22 (15), pp.3152-64. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddt172⟩. ⟨inserm-00826642⟩
- Laura Briñas, Stéphane Vassilopoulos, Gisele Bonne, Pascale Guicheney, Marc Bitoun. Role of dynamin 2 in the disassembly of focal adhesions. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2013, 91 (7), pp.803-809. ⟨10.1007/s00109-013-1040-2⟩. ⟨hal-02453840⟩
- Nicolas Vignier, Fatima Amor, Paul Fogel, Angélique Duvallet, Jérôme Poupiot, et al.. Distinctive Serum miRNA Profile in Mouse Models of Striated Muscular Pathologies. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8 (2), pp.e55281. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0055281⟩. ⟨hal-02336920⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Susana Quijano-Roy. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, laminopathies, and other nuclear envelopathies.. Handb Clin Neurol, 2013, 113, pp.1367-76. ⟨10.1016/B978-0-444-59565-2.00007-1⟩. ⟨inserm-00826557⟩
- Anne-Cécile Durieux, Stéphane Vassilopoulos, Jeanne Lainé, Bodvael Fraysse, Laura Briñas, et al.. A Centronuclear Myopathy - Dynamin 2 Mutation Impairs Autophagy in Mice. Traffic, 2012, 13 (6), pp.869-879. ⟨10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01348.x⟩. ⟨hal-02453822⟩
- Stéphane Chiron, Carole Tomczak, Alain Duperray, Jeanne Laine, Gisele Bonne, et al.. Dynamic interplay between human myoblasts and 3D fibrin-based matrix. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7 (4), pp.e36173. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0036173⟩. ⟨hal-00694186⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand, Laure Renou, Aurélie Papadopoulos, Maud Beuvin, Emmanuelle Lacène, et al.. DelK32-lamin A/C has abnormal location and induces incomplete tissue maturation and severe metabolic defects leading to premature death.. Human Molecular Genetics, 2012, 21 (5), pp.1037-48. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddr534⟩. ⟨hal-00672148⟩
- Allamand V, Laura Briñas, Pascale Richard, Tanya Stojkovic, Susana Quijano-Roy, et al.. ColVI-myopathies: where do we stand, where do we go?. Skeletal Muscle, 2011, 1 (1), pp.30. ⟨10.1186/2044-5040-1-30⟩. ⟨inserm-00630240⟩
- Mathieu Rederstorff, Perrine Castets, Sandrine Arbogast, Jeanne Lainé, Stéphane Vassilopoulos, et al.. Increased Muscle Stress-Sensitivity Induced by Selenoprotein N Inactivation in Mouse: A Mammalian Model for SEPN1-Related Myopathy. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6 (8), ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0023094⟩. ⟨hal-01716017⟩
- Patricia Khattar, Felix Friedrich, Gisèle Bonne, Lucie Carrier, Thomas Eschenhagen, et al.. Distinction Between Two Populations of Islet-1-Positive Cells in Hearts of Different Murine Strains. Stem Cells and Development, 2011, 20 (6), pp.1043-1052. ⟨10.1089/scd.2010.0374⟩. ⟨hal-03824036⟩
- Perrine Castets, Anne T. Bertrand, Maud Beuvin, Arnaud Ferry, Fabien Le Grand, et al.. Satellite cell loss and impaired muscle regeneration in selenoprotein N deficiency.. Human Molecular Genetics, 2011, 20 (4), pp.694-704. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddq515⟩. ⟨hal-00561402⟩
- B. Granger, L. Gueneau, V. Drouin-Garraud, Vincent Pedergnana, F. Gagnon, et al.. Modifier locus of the skeletal muscle involvement in Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Human Genetics, 2011, 129 (2), pp.149-159. ⟨10.1007/s00439-010-0909-1⟩. ⟨hal-03691751⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Claire L. Navarro, Susana Quijano-Roy, Anne T. Bertrand, Catherine Massart, et al.. Type B mandibuloacral dysplasia with congenital myopathy due to homozygous ZMPSTE24 missense mutation. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2011, ⟨10.1038/ejhg.2010.256⟩. ⟨hal-00611256⟩
- P. Castets, A.T. Bertrand, M. Beuvin, A. Ferry, F. Le Grand, et al.. O.3 Satellite cell loss is the pathomechanism leading to muscle atrophy in selenoprotein N deficiency. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2010, 20 (9-10), pp.598. ⟨10.1016/J.NMD.2010.07.012⟩. ⟨hal-02935581⟩
- Nadège Salvi, Aziz Guellich, Pierre Michelet, Alexandre Demoule, Morgan Le Guen, et al.. Upregulation of PPARβ/δ Is Associated with Structural and Functional Changes in the Type I Diabetes Rat Diaphragm. PLoS ONE, 2010, 5 (7), pp.e11494. ⟨10.1371/journal.pone.0011494⟩. ⟨inserm-02426556⟩
- Alain Lescure, Mathieu Rederstorff, Alain Krol, Pascale Guicheney, Valérie Allamand. Selenoprotein function and muscle disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects, 2009, 1790 (11), pp.1569 - 1574. ⟨10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.002⟩. ⟨hal-01716049⟩
- Alain Lescure, Mathieu Rederstorff, Alain Krol, Pascale Guicheney, Valérie Allamand. Selenoprotein function and muscle disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects, 2009, 1790 (11), pp.1569-1574. ⟨10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.002⟩. ⟨hal-03844559⟩
- Perrine Castets, Svetlana Maugenre, Corine Gartioux, Mathieu Rederstorff, Alain Krol, et al.. Selenoprotein N is dynamically expressed during mouse development and detected early in muscle precursors.. BMC Developmental Biology, 2009, 9 (1), pp.46. ⟨10.1186/1471-213X-9-46⟩. ⟨inserm-00610658⟩
- M. Rederstorff, V. Allamand, P. Guicheney, C. Gartioux, P. Richard, et al.. Ex vivo correction of selenoprotein N deficiency in rigid spine muscular dystrophy caused by a mutation in the selenocysteine codon. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36 (1), pp.237 - 244. ⟨10.1093/nar/gkm1033⟩. ⟨hal-01716066⟩
- M. Rederstorff, V. Allamand, P. Guicheney, C. Gartioux, Patrick Richard, et al.. Ex vivo correction of selenoprotein N deficiency in rigid spine muscular dystrophy caused by a mutation in the selenocysteine codon.. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36 (1), pp.237-44. ⟨10.1093/nar/gkm1033⟩. ⟨hal-00292612⟩
- Valérie Allamand, Laure Bidou, Masayuki Arakawa, Célia Floquet, Masataka Shiozuka, et al.. Drug-induced readthrough of premature stop codons leads to the stabilization of laminin alpha2 chain mRNA in CMD myotubes.. The Journal of Gene Medicine, 2007, epub ahead of print. ⟨10.1002/jgm.1140⟩. ⟨hal-00198869⟩
- P. Castets, S. Maugenre, Mathieu Rederstorff, A. Lescure, A. Krol, et al.. C.P.2.11 Expression of selenoprotein N in mice during development and in muscle regeneration. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2007, 17 (9-10), pp.847. ⟨10.1016/J.NMD.2007.06.287⟩. ⟨hal-02935590⟩
- Claude L. Charvet, Christophe Houbron, Ara Parlakian, Julien Giordani, Charlotte Lahoute, et al.. New Role for Serum Response Factor in Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Growth and Regeneration via the Interleukin 4 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Pathways. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2006, 26 (17), pp.6664-6674. ⟨10.1128/MCB.00138-06⟩. ⟨hal-03120739⟩
- V. Allamand, Patrick Richard, Et Al., A. Lescure, C. Ledeuil, et al.. A single homozygous point mutation in a 3'untranslated region motif of selenoprotein N mRNA causes SEPN1-related myopathy. EMBO Journal, 2006, 7, pp.450-454. ⟨hal-00094034⟩
- Laurent Ségalat, Karine Grisoni, Jonathan Archer, Cinthya Vargas, Anne Bertrand, et al.. CAPON expression in skeletal muscle is regulated by position, repair, NOS activity, and dystrophy.. Experimental Cell Research, 2005, 302 (2), pp.170-9. ⟨10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.09.007⟩. ⟨hal-00194444⟩
- L. Segalat, K. Grisoni, J. Archer, C. Vargas, Anne Bertrand, et al.. CAPON expression in skeletal muscle is regulated by position, repair, NOS activity, and dystrophy.. Experimental Cell Research, 2005, 302, pp.170-179. ⟨hal-00144038⟩
- Takuro Arimura, Anne Helbling-Leclerc, Catherine Massart, Shaida Varnous, Florence Niel, et al.. Mouse model carrying H222P-Lmna mutation develops muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy similar to human striated muscle laminopathies.. Human Molecular Genetics, 2005, 14 (1), pp.155-69. ⟨10.1093/hmg/ddi017⟩. ⟨hal-00165763⟩
- L. Bidou, I. Hatin, N. Pérez, V. Allamand, J.J. Panthier, et al.. Premature stop codons involved in muscular dystrophies show a broad spectrum of readthrough efficiencies in response to gentamicin treatment.. Gene Therapy, 2004, 11, pp.619-627. ⟨hal-02676851⟩
- Sylvie Besse, Valérie Allamand, Jean-Thomas Vilquin, Zhenlin Li, Christophe Poirier, et al.. Spontaneous muscular dystrophy caused by a retrotransposal insertion in the mouse laminin α2 chain gene. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2003, 13 (3), pp.216-222. ⟨10.1016/s0960-8966(02)00278-x⟩. ⟨hal-03824380⟩
- A Bosch, I Banchs, A Puig, Gilles Vergnaud, V Allamand, et al.. The EUROGEM map of human chromosome 12.. European Journal of Human Genetics, 1993, 2 (3), pp.226-7. ⟨hal-01160670⟩
- Ketty Schwartz, Catherine Chassagne, Kenneth Boheler. The molecular biology of heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 1993, 22 (4), pp.A30-A33. ⟨10.1016/0735-1097(93)90459-E⟩. ⟨hal-04275217⟩
- K Schwartz, Catherine Chassagne, L Carrier, K Boheler. [Left ventricular hypertrophy: molecular aspects].. Archives des Maladies du Coeur et des Vaisseaux, 1993, 86 Spec No 1, pp.73-5. ⟨hal-04275406⟩
- L Carrier, Catherine Chassagne, K Boheler, K Schwartz. [Molecular bases of cardiac aging].. La Presse Médicale, 1992, 21 (26), pp.1196-8. ⟨hal-04275777⟩
- K Boheler, Catherine Chassagne, X Martin, C Wisnewsky, K Schwartz. Cardiac expressions of alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chains and sarcomeric alpha-actins are regulated through transcriptional mechanisms. Results from nuclear run-on assays in isolated rat cardiac nuclei.. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267 (18), pp.12979-85. ⟨hal-04275047⟩
- L Carrier, K Boheler, Catherine Chassagne, D de la Bastie, C Wisnewsky, et al.. Expression of the sarcomeric actin isogenes in the rat heart with development and senescence.. Circulation Research, 1992, 70 (5), pp.999-1005. ⟨10.1161/01.res.70.5.999⟩. ⟨hal-04275109⟩
- Catherine Chassagne, Ketty Schwartz. Mapping of mRNA isoforms with an oligonucleotide probe: exonuclease VII compared with endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Research, 1992, 20 (12), pp.3256-3256. ⟨10.1093/nar/20.12.3256⟩. ⟨hal-04275102⟩
- Catherine Chassagne, Kenneth Boheler, Ketty Schwartz. Mise au point d’une méthode de transcription in vitro dans des noyaux isolés de myocytes de cœurs de rats contrôles et hémodynamiquement surchargés. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences de Paris, 1991, Tome 312 (Série III), pp.7-12. ⟨hal-04277305⟩
Conference papers
- J Hulot, L Deshayes, A Ruiz-Velasco, K Wahbi, A Muchir, et al.. The H222P-Lamin mutation induces heart failure via impaired mitochondrial calcium uptake in human cardiac laminopathy. ESC Congress 2024, Aug 2024, London, United Kingdom. ⟨10.1093/eurheartj/ehae666.3680⟩. ⟨hal-04764816⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. TREATABOLOME, A RARE DISEASES’ TREATMENT AWARENESS PROJECT. 9ème Journée nationale BRAIN -TEAM, Filière nationale de Santé Maladies rares du système nerveux central, Mar 2024, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04522201⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. ERDERA and opportunities for French genetics teams. 3rd Thursday of Clinical Genetics - “2025 France Genomic Medicine Initiative” (PFMG 2025) and the International Context, Feb 2024, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04460541⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Comment résoudre les impasses diagnostiques des maladies rares : partage systématique des données paneuropéennes et analyse collaborative : le projet Solve-RD. Journée thématique sur l'errance et l'impasse diagnostiques - Filière Filnemus, Filnemus, Dec 2023, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04319087⟩
- Kourtzas D, Rocio Nur Villar Quiles, Gartioux C, Allamand V. ECM characterization in novel cellular models for COL6-RD. Collagen VI International Research Summit, Fundacion Noelia, Nov 2023, San Sebastian, Spain. ⟨hal-04475051⟩
- Valérie Allamand, Soledad Monges, Corine Gartioux, Taratuto Ana Lia, Alix De Becdelièvre, et al.. A complex COL6A3 mutation identification: it takes an international village. Collagen VI International Research Summit, Fundacion Noelia, Nov 2023, San Sebastian, Spain. ⟨hal-04475082⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. 2002 - 2023 : l’Odyssée de… la Myologie. 20èmes Journées de la Société Française de Myologie, Societe Française de Myologie, Nov 2023, La Baule (France), France. ⟨hal-04319081⟩
- M Gomez Garcia, R. Garcia-Uzquiano, L. Le Goff, V. Manel, I. Dabaj, et al.. P431 Steroid treatment may change natural history in congenital laminopathies. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S160, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.372⟩. ⟨hal-04280227⟩
- J. de Winter, L. van de Vondel, Gisèle Bonne, T. Stojkovic, S. Elouej, et al.. P158 Heterozygous SPTAN1 frameshift mutations cause distal myopathy with neurogenic features. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S139, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.290⟩. ⟨hal-04280233⟩
- L. Benarroch, I. Nelson, T. Stojkovic, B Mohand Oumoussa, H. Madry, et al.. P166 Deciphering the genetic cause of oculopharyngodistal myopathy in a French cohort using Cas9-targeted long-read sequencing. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S141, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.298⟩. ⟨hal-04280249⟩
- V. Decostre, C. Chikhaoui, C. Vigouroux, A. Behin, G. Bassez, et al.. VP429 Impaired skeletal muscle strength in adult patients with laminopathies. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S159-S160, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.370⟩. ⟨hal-04280272⟩
- M. Okubo, A. Brull, M. Beuvin, N. Mougenot, V. Paradis, et al.. O03 In vivo gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S67, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.018⟩. ⟨hal-04280254⟩
- A. Merlet, E. Lacène, I. Nelson, G. Brochier, C. Labasse, et al.. P338 Clinical, morphological, and proteomic features of patients suspected of X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy (XMEA). 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston SC, United States. pp.S99, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.136⟩. ⟨hal-04280238⟩
- A. Atalaia, R. Thompson, L. Matalonga, C. Hernandez-Ferrer, A. Corvo, et al.. P192 The open-access treatabolome platform enhances the visibility of treatable and actionable genes in RD-connect's GPAP and other clinical diagnosis support tools. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston, United States. pp.S142, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.301⟩. ⟨hal-04280259⟩
- L. Benarroch, J. Madsen-Østerbye, M. Abdelhalim, K. Mamchaoui, J. Ohana, et al.. A robust and practical myogenic system to explore cellular and genomic features of muscle differentiation. 28th International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2023, Charleston, United States. pp.S158, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2023.07.363⟩. ⟨hal-04280205⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Martin Krahn. Concept de gènes actionnables et application dans le domaine neuromusculaire.. 25èmes Journées Neuromusculaires de Marseille, Sep 2023, Marseille, France. ⟨hal-04189737⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiological mechanisms of striated muscle Laminopathies. Ottawa NMD 2023 Conference, Sep 2023, Ottawa, Canada. ⟨hal-04189748⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. How to solve rare diseases: systematic pan-European data sharing and collaborative analysis: the Solve-RD project. 15th Congress of the European Paedriatric Neurology Society, European Paedriatric Neurology Society, Jun 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04189585⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiological mechanisms of striated muscle Laminopathies. European Meeting on Intermediate Filaments, Elly Hol, Jun 2023, Noorwijkerhout, Netherlands. ⟨hal-04189581⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Le Treatabolome : une base de donnée des traitements existant pour les maladies rares à l’échelle du gène/variant. Webinaire de la Filière en Santé Filnemus, May 2023, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04189577⟩
- Marine Leconte, Anne Bertrand, Zoheir Guesmia, Gisèle Bonne, Gisèle Bonne. DNA damage repair in LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189722⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Nathalie Mougenot, et al.. Challenges in gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04170075⟩
- Valérie Decostre, Cathy Chikhaoui, Corinne Vigouroux, Susana Quijano-Roy, Karim Wahbi, et al.. Quantification of skeletal muscle strength in laminopathies. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189561⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Julia Madsen-Østerbye, Mohamed Abdelhalim, Kamel Mamchaoui, Jessica Ohana, et al.. Validation of Myo-converted fi broblasts as a relevant model to study chromatin organization defects in striated muscle laminopathies. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189720⟩
- Rocio Garcia-Uzquiano, Marta Gomez-García de La Banda, Laure Le Goff, Veronique Manel, Ivana Dabaj, et al.. Steroid treatment may change natural history in congenital laminopathies. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189730⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Anne T. Bertrand, Maud Beuvin, Isabelle Nelson, Naïra Naouar, et al.. Identification of potential genetic modifi ers underlying phenotypic variability in a French family with striated muscle laminopathies. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189567⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Nathalie Mougenot, Valérie Paradis, et al.. Gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy (in vivo study). 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨hal-04189734⟩
- Noreen Khokhar, Cathleen Hagemann, Luca Pinton, Daniel Moore, Jean-Marie Cuisset, et al.. Investigating lineage-specifi c phenotypes of laminopathies using induced pluripotent stem cells. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189725⟩
- Daniel Moore, Heather Steele-Stallard, Luca Pinton, Valentina Lionello, Salma Jalal, et al.. Using patient iPSC-derived skeletal muscle models for development of a CRISPR-based exon removal therapeutic strategy. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189588⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Louise Benarroch, Marine Leconte, Maud Beuvin, Isabelle Nelson, et al.. Recent insights in the pathophysiological mechanisms of striated muscle laminopathies. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189555⟩
- Magali Seguret, C. Jouve, Z R. Al Sayed, C. Pereira, V. Ragot, et al.. Modeling of LMNA p.H222P mutation- related cardiomyopathy using human induced pluripotent stem cells. 4th International Meeting on Laminopathies, May 2023, Madrid, Spain. ⟨10.3233/JND-239001⟩. ⟨hal-04189728⟩
- Leslie Matalonga, Ida Paramonov, Wouter Steyaert, Heba Morsy, Daniel Danis, et al.. SNV-InDel working group: Results and lessons learned from the analysis of 22,035 exomes and genomes from 6 European reference networks. Solve-RD, Solving the unsolved Rare Diseases, Final Meeting 2023, Apr 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04086234⟩
- Isabelle Nelson, German Demidov, Enzo Cohen, Aurélien Perrin, Mireille Cossée, et al.. Solve-NMD in Paris: Project results. Solve-RD, Solving the unsolved Rare Diseases, Final Meeting 2023, Apr 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04086236⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The Treatabolome flags treatable genes and variants: an emerging concept. NC-IUPHAR Symposium April 2023, Servier, Apr 2023, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04189545⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, Martin Krahn. Linking actionable genes to the treatabolome in myopathies. NC-IUPHAR Symposium April 2023, Apr 2023, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04078530⟩
- Leslie Caron, Allamand V. Modelling LAMA2-CMD to explore physiopathology and therapeutic options. EJPRD Workshop: LAMA2-Muscular Dystrophy: Paving the road to therapy, Mar 2023, Barcelone, Spain. pp.16-22, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2024.01.001⟩. ⟨hal-04475069⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Table Ronde: Quel avenir pour la recherche sur les maladies rares ?. Dix ans de contribution de l’ANR au domaine des maladies rares, Nov 2022, Paris, France. ⟨hal-03984507⟩
- Marine Leconte, Gisèle Bonne, Anne T Bertrand. Etude des dommages de l'ADN dans la dystrophie musculaire congénitale liée à LMNA. 19èmes Journées de la Société Française de Myologie, Nov 2022, Toulouse, France. ⟨hal-04004845⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The clinico-genetic spectrum of Lamin A/C gene (LMNA) mutations. A hybrid workshop on the nuclear envelope, mechanobiology and rare disease, Oct 2022, Hybrid conference, Singapore. ⟨hal-03984506⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Ludovic Arandel, Gisèle Bonne. Origin of the increased severity of LMNA-related muscular dystrophy compared with Emery-Dreyfuss muscular dystrophy. A hybrid workshop on the nuclear envelope, mechanobiology and rare diseases, Oct 2022, Singapore, Singapore. ⟨hal-04004827⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Identification of genetic modifiers modulating the disease severity of LMNA-Congenital Muscular Dystrophy (LMNA-CMD). European Network for Laminopathies Meeting, Sep 2022, Bologna, Italy. ⟨hal-03984504⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Nathalie Mougenot, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathies. European Network for Laminopathies Meeting, Sep 2022, Bologna, Italy. ⟨hal-04003052⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Laura Julien, et al.. Gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy. 12th French-Japanese Workshop on Neuromuscular Diseases, Gisèle Bonne; Ichizo Nishino, Sep 2022, Giverny, France. ⟨hal-03989233⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Gisèle Bonne, Anne T Bertrand. Development of gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy. Cure CMD scientific and family conference, Jun 2022, Nashville, United States. ⟨hal-04004853⟩
- Valérie Allamand. Therapeutic options for premature termination codon mutations in COLVI-related dystrophies. . Cure CMD scientific and family conference, Jun 2022, Visio conference, France. ⟨hal-04029236⟩
- Anne T Bertrand. Current status of gene therapies development in Laminopathy. 253rd ENMC International Workshop: Striated Muscle Laminopathies, Jun 2022, Hoofddorp, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03989257⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Discussion needed on how to define and select non-clinical biomarkers. 253rd ENMC International Workshop: Striated Muscle Laminopathies, G Bonne, S Quijano-Roy, L Maggi, C Bonnemann, Jun 2022, Hoofddorp, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984500⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Striated muscle laminopathies: Modifier variants. 253rd ENMC International Workshop: Striated Muscle Laminopathies, G Bonne, S Quijano-Roy, L Maggi, C Bonnemann, Jun 2022, Hoofddorp, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984494⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Patients’ registries: present and future. 253rd ENMC International Workshop: Striated Muscle Laminopathies, G Bonne, S Quijano-Roy, L Maggi, C Bonnemann, Jun 2022, Hoofddorp, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984497⟩
- Valérie Allamand. Therapeutic options for premature termination codon mutations in COLVI-related dystrophies. . Noelia Fundacion - Collagen VI meeting 2022, Jun 2022, Visio conference, France. ⟨hal-04029241⟩
- Isabelle Nelson, German Demidov, Enzo Cohen, Aurélien Perrin, Mireille Cossée, et al.. Cold Case (Season II): TTN deletion described after CNV analyses. Solve-RD Annual Meeting 2022, Apr 2022, Virtual conference, Germany. ⟨hal-03989193⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Striated muscle laminopathies, from gene defects to pathomechanisms and therapeutic approaches: what are we missing?. Discovering a cure for LMNA: Current strategies, crazy ideas and future collaborations, Apr 2022, Virtual conference, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984492⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Identification of genetic modifiers modulating the disease severity of LMNA-Congenital Muscular Dystrophy (LMNA-CMD). MDUK Muscles Matter online seminar series Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD), Mar 2022, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03984491⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The Treatabolome flags treatable genes and variants: an emerging concept. ERN-Euro-NMD-Eurordis CETF symposium, Nov 2021, Virtual conference, France. ⟨hal-03984489⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Molecular pathophysiological mechanisms of Cardiac Laminopathies. British Heart Fondation Centre virtual 2021 Symposium, Nov 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03984487⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Striated muscle of Laminopathies, Scientific advances for the development of treatments. LMNACardio Foundation meeting, Oct 2021, Virtual conference, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984485⟩
- A Atalaia, C Hernandez Ferrer, A Corvó, L Matalonga, R Thompson, et al.. The Treatabolome flags treatable genes and variants: an emerging concept. ERN Euro-NMD Webinar on Treatabolome, Oct 2021, Webinar, Germany. ⟨hal-03989142⟩
- Sanzana Hoque, Rana Soylu Kucharz, Valérie Allamand, Marie Sjögren, Kinga Gawlik, et al.. Assessment of muscle regeneration in the R6/2 mouse model of huntington’s disease. Meeting of the European-Huntington's-Disease-Network (EHDN), Sep 2021, ELECTR NETWORK, Sweden. pp.A8.2-A8, ⟨10.1136/jnnp-2021-EHDN.19⟩. ⟨hal-03867574⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. History and discovery of Laminopathy , Scientific advances for the development of treatments. Symposium on Rare Diseases in Puerto Rico from the Capitol, Jul 2021, Virtual conference, Puerto Rico. ⟨hal-03984484⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou. Emery-Dreifuss disease and related disorders. XXII Forum of Neuromuscular diseases of the Scientific Department of Neuromuscular Diseases of the Brazilian Academy of Neurology, Jun 2021, Virtual conference, Brazil. ⟨hal-03988621⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. LMNA (Laminopathy) Research. Cure-CMD: 2021 Virtual SciFam, May 2021, Virtual conference, United States. ⟨hal-03984482⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Solve-RD: Un projet Européen visant à réduire l’errance diagnostique. Eunjeux et Défis de la Recherche dans les Maladies Rares - Fondation Malaides Rares, May 2021, Conference - Online., France. ⟨hal-03984480⟩
- C. Hernandez-Ferrer, A. Corvó, L. Matalonga, R. Thompson, L. Carmody, et al.. Treatabolome database: towards enhancing Rare Diseases’ treatment visibility. Solve-RD Annual Meeting 2021, Apr 2021, Virtual conference, Germany. ⟨hal-03988747⟩
- Isabelle Nelson, Enzo Cohen, Rabah Ben Yaou, France Leturq, Juliette Nectoux, et al.. Cold Case: Patient with only one CAPN3 variant. Solve-RD Annual Meeting 2021, Apr 2021, Virtual conference, Germany. ⟨hal-03988006⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Ludovic Arandel, Gisèle Bonne. Gene therapy for LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. Cure CMD scientific and family conference, Nov 2020, Virtual conference, United States. ⟨hal-04004849⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Actions Recherche. Journée de la Filière en Santé Maladies Neuromusculaire Rares, Filnemus, Oct 2020, Conference - Online., France. ⟨hal-03984478⟩
- R. Villar Quiles, S. Donkevoort, A. de Becdelievre, V. Allamand, V. Jobic, et al.. Clinical and molecular spectrum associated with COL6A3 c.7447A>G variant: elucidating its role in Collagen VI-related myopathies. 25th International Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Sep 2020, ELECTR NETWORK, France. pp.S105-S106, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2020.08.202⟩. ⟨hal-03867614⟩
- E. Cohen, I. Nelson, C. Gartioux, M. Beuvin, Z. Mezdari, et al.. Whole exome sequencing identifies compound heterozygous missense variants in the LOXL4 gene: a novel candidate cause of contractural myopathy. 25th International Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Sep 2020, ELECTR NETWORK, France. pp.S47, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2020.08.007⟩. ⟨hal-03867603⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Solved-RD WP3 progress update. Solve-RD Annual Steering Committee Meeting, Sep 2020, Virtual Conference, Germany. ⟨hal-03984472⟩
- E Cohen, I Nelson, C Gartioux, M Beuvin, Z Mezdari, et al.. Whole exome sequencing identifies compound heterozygous missense variants in the LOXL4 gene: a novel candidate cause of contractural myopathy. New Directions in Skeletal Muscle Biology, Jun 2020, Virtual conference (Covid), United States. ⟨hal-04004866⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The Concept of Treatabolome. ESHG 2020.2 - European Human Genetics Virtual Conference, Jun 2020, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03984475⟩
- Antonio Atalaia, Gisèle Bonne. WP3 Task 3. Treatabolome. Solve-RD Annual Meeting, Mar 2020, Barcelona, Spain. ⟨hal-03986988⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Laminopathy of the striated muscle: from the gene defects to therapeutic approaches. Invited Seminar by Prof I Perez at Unidad de Terapia Génica, Instituto de Investigación de Enfermedades Raras, Feb 2020, Madrid, Spain. ⟨hal-03984464⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Isabelle Nelson, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, Zaineb Mezdari, et al.. Compound heterozygous mutations in the LOXL4 gene: a novel cause of contractural myopathy. ASSISES DE GÉNÉTIQUE HUMAINE ET MÉDICALE, Jan 2020, Tours, France. ⟨hal-03986985⟩
- L Pinton, D Moore, H Steele-Stallard, S Sarcar, T Ozdemir, et al.. Modelling skeletal muscle laminopathies with human iPS cells and bio-engineered skeletal muscles: Prospects for genetic therapies. ESGCT 27th Annual Congress in collaboration with SETGyc Meeting, Oct 2019, Barcelona, Spain. pp.OR11. ⟨hal-03983924⟩
- M. Gomez Garcia de la Banda, D. Natera-de Benito, I. Dabaj, R. Ben Yaou, C. Ortez, et al.. Steroid treatment may change natural history in young children with LMNA mutations and dropped head syndrome. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhagen, Denmark. pp.S141, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.370⟩. ⟨hal-03973469⟩
- V. Bolduc, A. Foley, H. Solomon Degefa, A. Sarathy, S. Donkervoort, et al.. A novel target for splice-modulating therapies: a common pseudoexon-inducing mutation that causes a severe collagen VI-related muscular dystrophy. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhague, Denmark. pp.S40-S41, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.028⟩. ⟨hal-03867622⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. European Network for Laminopathies management: Network Activities. Satellite Meeting European Network for Laminopathies Meeting, Sep 2019, Kings College, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03984462⟩
- Corinne Vigouroux, Rabah Ben Yaou, Isabelle Jeru, Caroline Stalens, Olivier Lascols, et al.. LMNA-linked lipodystrophy : new insight on cardiovascular phenotypes. 9th UK Nuclear Envelope Disease and Chrmatin Organisation Meeting / 3rd International Meeting on Laminopathies, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986922⟩
- Karim Wahbi, Rabah Ben Yaou, Caroline Stalens, Corinne Vigouroux, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Risk stratification for sudden death in laminopathies. 9th UK Nuclear Envelope Disease and Chrmatin Organisation Meeting / 3rd International Meeting on Laminopathies, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986944⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand. Haploinsufficiency and dominant negative effects of mutant lamin A/C contribute to the severity of L-CMD compared with EDMD. Satellite Meeting European Network for Laminopathies Meeting, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986911⟩
- K Wahbi, R Ben Yaou, E Gandjbakhch, F Anselme, T Gossios, et al.. New risk prediction score for life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias in laminopathies. Congress of the European-Society-of-Cardiology (ESC) / World Congress of Cardiology, Aug 2019, Paris, France. pp.5164. ⟨hal-03983930⟩
- Astrid Brull. WT lamin A/C overexpression combined with mutant lmna knock-down extends lifespan in a murine model of LMNA-congenital muscular dystrophy. Cure CMD scientific and family conference, Jul 2019, Chicago, United States. ⟨hal-03986978⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Monika Zwerger, Colin Stewart, et al.. Combination of haploinsufficiency and dominant negative effects of mutant lamin A/C are responsible for the increased severity of L-CMD compared with EDMD.. 11TH EUROPEAN INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT MEETING EUROIF AND COST EUROCELLNET MEETING, Jun 2019, Turku, Finland. ⟨hal-03986896⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Laminopathy of the striated muscle: from the gene defects to therapeutic approaches. 11TH EUROPEAN INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT MEETING EUROIF AND COST EUROCELLNET MEETING 2019, Jun 2019, Turku, Finland. ⟨hal-03984461⟩
- Astrid Brull, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Gisèle Bonne, Anne T. Bertrand. miRNA-processing pathway is impaired in skeletal muscle laminopathies. 11TH EUROPEAN INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT MEETING EUROIF AND COST EUROCELLNET MEETING, Jun 2019, Turku, Finland. ⟨hal-03986899⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Laminopathy of the striated muscle: from the gene defects to therapeutic approaches. 26th Wilhelm Bernhard Workshop on the Cell Nucleus, May 2019, Dijon, France. ⟨hal-03984458⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Laminopathy of the striated muscle: from the gene defects to therapeutic approaches. Séminaire UMR Inserm 1011 – Université Lille, Apr 2019, Lilles, France. ⟨hal-03984453⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. TOWARDS THERAPY: REGISTRIES, BIOBANKS, TREATABLE VARIANTS. Solve-RD Annual Meeting, Feb 2019, Radboud University Medical Center (UMC), Nijmegen,, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03984450⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou. The Laminopathies. Journée de recherche clinique du CNMR Ile de France (Hôpital Necker Enfants Malades), Dec 2018, Paris, France. ⟨hal-03986882⟩
- Anne T Bertrand. Maintenance of nucleoplasmic lamin A/C during myoblast differentiation induces nuclear fusion in LMNA-related congenital myopathy. 2nd Meeting of the European Network for Laminopathies, Nov 2018, Bologna (ITALY), Italy. ⟨hal-03986767⟩
- Yvan De Feraudy, Rabah Ben Yaou, Karim Wahbi, France Leturcq, Helge Amthor, et al.. Residual very low dystrophin levels mitigate dystrophinopathy towards Becker muscular dystrophy. 25th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2018, Mendoza (Argentina), Argentina. ⟨hal-04015244⟩
- Malek Kammoun, Vladimir Veksler, Jérôme Piquereau, Gisèle Bonne, Isabelle Nelson, et al.. KLF10 regulates skeletal muscle metabolism in mice. American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Annual Meeting, American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, Sep 2018, Montréal, Canada. ⟨hal-01981364⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Keynote Lecture : Laminopathies from the first mutation to therapeutic avenues. Rare Diseases Summer School - Rare Disease Initiative Zürich, Jul 2018, Kartause Ittingen, Warth, Switzerland. ⟨hal-03984433⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Striated muscle Laminopathies from gene defects to pathophysiology mechanisms. 13th Meeting of the Mediterranean Society of Myology in connection with the 2nd Congress of the Turkish Neuromuscular Society, Jun 2018, Avanos, Cappadocia, Turkey. ⟨hal-03984438⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Laminopathies: unveiling the pathophysiology. Gordon Research Conference on Intermediate filaments, Jun 2018, Rennaissance Tuscany Il Ciocco, Italy. ⟨hal-03984444⟩
- Margot Saunier, Benjamin Nayagom, Guillaume Dubois, Valérie Allamand. Shear Wave elastography assessment of muscle stiffness changes in KI-Col6a2 mice. 11th Japanese-French Workshop, Jun 2018, Tokyo, Japan. ⟨hal-04029253⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The Laminopathies. Invited Seminar by Porf Alessandra Ferlini, May 2018, Ferrara, Italy. ⟨hal-03984446⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiology of LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. 4th Joint Meeting Belgian-Dutch Neuromuscular Study Group & German Reference Center for Neuromuscular Diseases, May 2018, Valls, Netherlands. ⟨hal-03983950⟩
- Jocelyn Laporte, Raphael Schneider, Edoardo Malfatti, Gisèle Bonne, France Leturcq, et al.. Analyse intégrée du grand projet de séquençage MYOCAPTURE d’identification de nouveaux gènes de myopathies. 9èmes Assises de Génétique Humaine et Médicale, Jan 2018, Nantes, France. ⟨hal-03986850⟩
- Valérie Allamand, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Corine Gartioux, Fanny Roth, et al.. A new gene for myopathies with prominent contractures?. Journée Filnemus 2017, Nov 2017, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04029252⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou. The French OPALE registry update. LMNA consortium Meeting at Institute of Health Carlos III – ISCIII, Oct 2017, Madrid, Spain. ⟨hal-03986859⟩
- Astrid Brull. Gene therapy for LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. LMNA consortium Meeting atInstitute of Health Carlos III – ISCIII, Oct 2017, Madrid, Spain. ⟨hal-03986864⟩
- Catherine Coirault. Lamin A/C is crucial for skeletal muscle plasticity. 14th IIM (Interuniversity Institute of Myology) meeting, Oct 2017, Assisi, Italy. ⟨hal-03972582⟩
- J. Bohm, R. Schneider, E. Malfatti, V. Schartner, X. Lornage, et al.. Integrated analysis of the large-scale sequencing project ``Myocapture'' to identify novel genes for myopathies. 22nd International Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. pp.S195, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.367⟩. ⟨hal-01741738⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Maintenance of nucleoplasmic lamin A/C during myoblast differentiation induces nuclear fusion in LMNA-related congenital myopathy.. The Pleiotropic Nuclear Envelope, John McIntyre Conference Centre, University of Edinburgh, Aug 2017, Edinburgh (Ecosse), United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03972911⟩
- Valérie Allamand. From Iowa City to Paris: From sarcolemma to extracellular matrix. Muscle Membrane Serendipity: Past, Present & Future, Jul 2017, Iowa City, United States. ⟨hal-04029249⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand. Development of gene therapy for LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. Cure CMD scientific and family conference, Jul 2017, Washington DC, United States. ⟨hal-04004859⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiology of LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. The Nuclear Lamina and nuclear organization. Cost School & The Batsheva de Rothschild Seminar., Jun 2017, Yearim, Israel. ⟨hal-03972905⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiology of striated muscle Laminopathies. 2nd International Meeting on Laminopathies, Giovanna Lattanzi, Apr 2017, Bologna, Italy. ⟨hal-03972901⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. Insights in the pathophysiology of striated muscle Laminopathies. Workshop of COST Action CA15214 An Integrative Action for Multidisciplinary Studies on Cellular Structural Networks, Pavel Hodzak, Mar 2017, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-03972189⟩
Poster communications
- Dimitrios Kourtzas, Rocio Nur Villar-Quiles, Satish Moparthi, C Gartioux, Stéphane Vassilopoulos, et al.. Refined pro-fibrotic cellular models for detailed extracellular matrix analysis in collagen VI-related dystrophies. 8th International Congress in Myology, Apr 2024, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04602727⟩
- Jonathan De Winter, Liedewei van De Vondel, Gisèle Bonne, Tanya Stojkovic, Sahar Elouej, et al.. Heterozygous SPTAN1 frameshift mutations cause distal myopathy with neurogenic features. Solve-RD, Solving the unsolved Rare Diseases, Final Meeting 2023, Apr 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04086227⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Corinne Métay, Marco Savarese, Rabah Ben Yaou, German Demidov, et al.. Titin copy number variations associated with dominant inherited phenotypes. Solve-RD, Solving the unsolved Rare Diseases, Final Meeting 2023, Apr 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04086226⟩
- Mridul Johari, Daphne Wijnbergen, Alaa Khan, Pedro Machado, Henry Houlden, et al.. Elucidating the molecular biology of Inclusion body Myositis through multi-omics analysis. Solve-RD, Solving the unsolved Rare Diseases, Final Meeting 2023, Apr 2023, Prague, Czech Republic. ⟨hal-04086230⟩
- Rocio García-Uzquiano, Marta Gómez-García de la Banda, Laure Le Goff, Véronique Manel, Ivana Dabaj, et al.. Expérience de l’utilisation des corticoïdes dans les laminopathies de l’enfant. 32 ème congrès de la Société Française de Neurologie Pédiatrique, Marseille, Jan 2023, Marseille (FRANCE), France. ⟨hal-04015316⟩
- Aurélien Perrin, Charles Van Goethem, Corinne Métay, Raul Juntas Morales, Françoise Chapon, et al.. Analyses fonctionnelles et études de corrélation phénotype-génotype chez des patients suspects de titinopathie. 19èmes Journées de la Société Française de Myologie, Nov 2022, Toulouse, France. ⟨hal-04004837⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Frédéric Anselme, Annachiara de Sandre-Giovannoli, Emmanuelle Campanna-Salort, Philippe Charron, et al.. OPALE: A patient registry for Laminopathies and Emerinopathies in France.. 19èmes Journées de la Société Française de Myologie, Nov 2022, Toulouse, France. ⟨hal-04003074⟩
- Nur Villar-Quiles, Corinne Métay, Corine Gartioux, Tanya Stojkovic, Valérie Allamand. Optimisation du rendement diagnostique des COL6-RM grâce au développement de nouveaux modèles cellulaires. 9° Journée Annuelle FILNEMUS (2022), Oct 2022, Paris, France. ⟨hal-04029234⟩
- L. Benarroch, A. Bertrand, M. Beuvin, I. Nelson, N. Naouar, et al.. Identification of potential genetic modifiers underlying phenotypic variability in a French family with striated muscle laminopathies. 27th International Hybrid Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2022, Halifax, Canada. Neuromuscular Disorders, 32, pp.S108, 2022, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2022.07.273⟩. ⟨hal-03983832⟩
- Gisèle Bonne, D Moore,, V Lionello,, S Jalal,, Hs Stallard,, et al.. Editing the Nuclear Envelope: Using Human iPS Cells and CRISPR-Cas Technology to Develop Novel Therapies for Skeletal Muscle Laminopathies. 29th Annual Congress of the European-Society-of-Gene-and-Cell-Therapy (ESCGT), Oct 2022, Edinburgh, Ecosse, United Kingdom. Hum. Gene Ther., 33 (23-24), pp.A208, 2022. ⟨hal-03983868⟩
- R. Ben Yaou, F. Anselme, A. de Sande-Giovannoli, E. Campanna-Salort, P. Charron, et al.. OPALE: a patient registry for laminopathies and emerinopathies in France. 27th International Hybrid Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2022, Halifax, Canada. Neuromuscular Disorders, 32, pp.S112, 2022, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2022.07.292⟩. ⟨hal-03983839⟩
- A Merlet, E Lacène, Isabelle Nelson, G Brochier, C Labasse, et al.. Clinical, morphological, and proteomic features of patients suspected of X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy (XMEA). World Muscle Society 2023, Oct 2022, Charleston Caroline du Sud, United States. ⟨hal-04472909⟩
- Rana Soylu-Kucharz, Sanzana Hoque, Valérie Allamand, Marie Sjögren, Kinga Gawlik, et al.. A23 Skeletal muscle regeneration is altered in the r6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. EHDN 2022 Plenary Meeting, Bologna, Italy, Abstracts, Sep 2022, Bologna, Italy. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, pp.A8.3-A9, ⟨10.1136/jnnp-2022-ehdn.23⟩. ⟨hal-04029246⟩
- Rabah Ben Yaou, Frédéric Anselme, Emmanuelle Campanna-Salort, Philippe Charron, Cathy Chikhaoui, et al.. OPALE: A patient registry for Laminopathies and Emerinopathies in France.. 7th international congress of Myology - Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04003067⟩
- Mariko Okubo, Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Nathalie Mougenot, Valérie Paradis, et al.. Gene therapy for striated muscle laminopathy. 7th international congress of myology - Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04004819⟩
- Valérie Allamand, Maria Soledad Monges, Corine Gartioux, Ana Lia Taratuto, Alix De Becdelièvre, et al.. A complex COL6A3 mutation identification: it takes an international village. Myology 2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04029226⟩
- Louise Benarroch, Anne T. Bertrand, Maud Beuvin, Isabelle Nelson, Floriane Simonet, et al.. Identification of potential genetic modifiers underlying phenotypic variability in a French family with striated muscle laminopathies. 7th international congress of myology - Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04004811⟩
- Alexandre Prola, Laurence Neff, Olivier Dorchies, Valérie Allamand, Frederic Relaix, et al.. Metabolic regulation of adult muscle stem cells. Myologie 2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04029216⟩
- Astrid Brull, Maud Beuvin, Isabelle Nelson, Gisèle Bonne, Anne T. Bertrand. miRNA-processing pathway is impaired in striated muscle laminopathies. 7th international congress of myology: Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice Acropolis, France. ⟨hal-03992829⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Isabelle Nelson, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, Zaineb Mezdari, et al.. LOXL4 loss-of-function: a novel cause of matrisome-related disease. 7th international congress of myology - Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04003081⟩
- Anne T Bertrand. miRNA-processing pathway is impaired in skeletal muscle laminopathies. Myology 2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04170057⟩
- Isabelle Nelson, Enzo Cohen, German Demidov, Aurélien Perrin, Mireille Cossée, et al.. Solve-RD, solving unsolved cold cases: TTN deletion described thanks to a systematic Copy Number Variant/Structural Variant (CNV/SV) reanalysis. 7th international congress of myology - Myology2022, Sep 2022, Nice, France. ⟨hal-04004807⟩
- A Atalaia, C Hernandez Ferrer, A Corvó, L Matalonga, R Thompson, et al.. Treatabolome database: current state and new developments towards enhancing rare disease treatment visibility. Solve-RD Annual Meeting 2022, Apr 2022, Virtual Conference, Germany. ⟨hal-03989222⟩
- Corinne Métay, Valérie Allamand, Valérie Jobic, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, et al.. Corrélation entre variants du gène TNXB et la coexistence de 2 types de syndromes d’Ehlers-Danlos dans une même famille. 11èmes Assises de Génétique Humaine et Médicale, Feb 2022, Rennes, France. ⟨hal-04029242⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Louise Benarroch, Khadija Chikhaoui, et al.. Lamin A/C Assembly Defects in LMNA-Congenital Muscular Dystrophy Is Responsible for the Increased Severity of the Disease Compared with Emery–Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. 18èmes Journées de la Société Française de Myologie, Nov 2021, Saint Etienne, France. ⟨hal-03989163⟩
- G. Moulay, I. Nelson, J. Lainé, E. Cohen, M. Lemaître, et al.. The alpha2-subunit of the AP2 clathrin adaptor as the causal gene in an atypical myopathy with granulofilamentous inclusions. 26th International Congress of the World Muscle Society (WMS), Sep 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 31, pp.S141-S142, 2021, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2021.07.326⟩. ⟨hal-03983816⟩
- Gilles Moulay, Isabelle Nelson, Jeanne Lainé, Enzo Cohen, Mégane Lemaître, et al.. The α2-subunit of the AP2 clathrin adaptor as a new causal gene in an atypical myopathy with granulofilamentous inclusions. Congress of the World Muscle Society, Sep 2021, Virtual, France. 2021. ⟨hal-03967904⟩
- M Vecten,, E Pion,, Rj Morales,, D Sternberg,, J Rendu,, et al.. Objective evaluation of clinical actionability for genes involved in myopathies: 34 promising genes. 26th International Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Sep 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 31 (Suppl 1), pp.LBP.14, 2021. ⟨hal-03983901⟩
- S. Elouej, I. Nelson, E. Cohen, R. Ben Yaou, A. Isapof, et al.. Functional validation of a novel variant of the SPTAN1 gene identified in a family with distal motor myopathy with nerve involvement. 26th International Congress of the World Muscle Society (WMS), Sep 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 31, pp.S72, 2021, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2021.07.100⟩. ⟨hal-03983822⟩
- A. Atalaia, R. Thompson, L. Matalonga, C. Hernandez-Ferrer, A. Corvo, et al.. The Treatabolome flags treatable genes and variants: an emerging concept. 26th International Congress of the World Muscle Society (WMS), Sep 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 31, pp.S146-S147, 2021, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2021.07.344⟩. ⟨hal-03983828⟩
- Carles Hernandez-Ferrer, Leslie Matalonga, Rachel Thompson, Leigh Carmody, Davide Piscia, et al.. The Treatabolome Database and Platform: enhancing Rare Diseases’ treatment visibility.. European Human Genetics Virtual Conference 2021, Aug 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03988844⟩
- C Hernandez-Ferrer,, A Corvo,, L Matalonga,, R Thompson,, L Carmody,, et al.. Treatabolome database: towards enhancing Rare Diseases' treatment visibility. 54th European Society of Human Genetics (ESHG) Conference, Aug 2021, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Eur. J. Hum. Genet., 30 (Suppl 1), pp.P17.076.C, 2022. ⟨hal-03983893⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Monika Zwerger, Colin Stewart, et al.. Combination of haploinsufficiency and dominant negative effects of mutant lamin A/C are responsible for the increased severity of L-CMD compared with EDMD. Cure-CMD: 2021 Virtual SciFam, May 2021, Virtual conference, United States. ⟨hal-03988774⟩
- Emmanuelle Lacène, Maud Beuvin, Teresinha Evangelista, Norma Romero, Bruno Cadot. Skeletal Muscle Atlas: a tool for the muscle community. Congress of the World Muscle Society, Sep 2020, Virtual, France. ⟨hal-03968094⟩
- Mr Luca Pinton, Ms Heather Steele-Stallard, Mr Daniel Moore, Dr Shilpita Sarcar, Dr Tanel Ozdemir, et al.. High-fidelity modelling of skeletal muscle laminopathies using LMNA-mutant human iPS cells and bioengineered muscles for mutation-specific therapy development. 25th International Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Sep 2020, Vituel, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 30, pp.S171, 2020, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2020.09.022⟩. ⟨hal-03983805⟩
- A Atalaia, R Thompson, A Corvo, L Carmody, D Piscia, et al.. Treatabolome: a rare diseases treatment awareness project. ESHG 2020.2 - European Human Genetics Virtual Conference, Jun 2020, Virtual conference, United Kingdom. Eur. J. Hum. Genet., 28 (Suppl 1), pp.P18.57.A, 2020. ⟨hal-03983888⟩
- A Atalaia, R Thompson, A Corvo, L Carmody, D Piscia, et al.. Treatabolome: a rare diseases treatment awareness project. 10th European Conference on Rare Diseases & Orphan Products 2020., May 2020, Virtual conference, Belgium. ⟨hal-03986996⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Isabelle Nelson, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, Zaineb Mezdari, et al.. Whole exome sequencing identifies compound heterozygous missense variants in the LOXL4 gene: a novel candidate cause of contractural myopathy. Solve-RD Annual Meeting, Mar 2020, Barcelona, Spain. ⟨hal-03986992⟩
- M Gomez-Garcia de la Banda, I Dabaj, R Ben Yaou, N Clarke, A Nascimento, et al.. LES CORTICOIDES ORAUX, UNE OPTION THERAPEUTIQUE DANS LES LAMINOPATHIES CONGENITALES ?. 17èmes Journées annuelles de la Société Françasie de Myologie, Nov 2019, Marseille, France. ⟨hal-03986950⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Louise Benarroch, Monika Zwerger, et al.. Haploinsufficiency and dominant negative effects of mutant lamin A/C both contribute to the increased severity of L-CMD compared with EDMD.. 17èmes Journées annuelles de la Société Françasie de Myologie, Nov 2019, Marseiile, France. ⟨hal-03986960⟩
- Astrid Brull, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Feriel Azibani, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Wild-type lamin A overexpression combined with mutant Lmna knock-down extends lifespan in a murine model of LMNA-congenital muscular dystrophy. 17èmes Journées annuelles de la Société Françasie de Myologie, Nov 2019, Marseille, France. ⟨hal-03986971⟩
- Astrid Brull, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Gisèle Bonne, Anne T Bertrand. miRNA-processing pathway is impaired in skeletal muscle laminopathies. 17èmes Journées annuelles de la Société Françasie de Myologie, Nov 2019, Marseille, France. ⟨hal-03986975⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Isabelle Nelson, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, Zaineb Mezdari, et al.. Compound heterozygous mutations in the LOXL4 gene: a novel cause of contractural myopathy. 17èmes Journées annuelles de la Société Françasie de Myologie, Nov 2019, Marseille, France. ⟨hal-03986965⟩
- A Brull, I Nelson, M Beuvin, F Azibani, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Wild-type lamin A overexpression combined with mutant Lmna knock-down extends lifespan in a murine model of LMNA-congenital muscular dystrophy. ESGCT 27th Annual Congress in collaboration with SETGyc Meeting, Oct 2019, Barcelona, Spain. Hum. Gene Ther., 30 (11), pp.P484, 2019. ⟨hal-03983916⟩
- S. Torelli, D. Scaglioni, V. Sardone, J. Domingos, A. Jones, et al.. Correlation between dystrophin espression and clinical phenotype using high-throughput digital immunoanalysis in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhagen, Denmark. 29, pp.S90, 2019, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.199⟩. ⟨hal-03973454⟩
- M. Beuvin, E. Lacène, C. Labasse, G. Brochier, A. Madelaine, et al.. Morphological, ultrastructural and western blot analysis in adult and child with PLEC1-related myopathy. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhagen, Denmark. 29, pp.S138, 2019, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.359⟩. ⟨hal-03973473⟩
- R. Ben Yaou, T. Stojkovic, Mathieu Cerino, F. Duval, R. Juntas-Morales, et al.. LGMD, exercise intolerance, ptosis, ophthalmoplegia and dermatologic features: the phenotypic pleiotropy of plectinopathies in 8 French families. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhagen, Denmark. 29, pp.S140, 2019, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.366⟩. ⟨hal-03973478⟩
- T. Stojkovic, A. de Becdelievre, S. Quijano-Roy, V. Jobic, C. Ledeuil, et al.. Sequencing the fibroblasts COL6A1-3 cDNAs versus gene panel genomic DNA in the diagnostic of COLVI related myopathies. 24th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2019, Copenhagen, Denmark. Neuromuscular Disorders, 29, pp.S192-S193, 2019, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2019.06.543⟩. ⟨hal-04004872⟩
- Luca Pinton, Heather Steele-Stallard, Daniel Moore, Shilpita Sarcar, Tanel Ozdemir, et al.. MODELLING SKELETAL MUSCLE LAMINOPATHIES USING HUMAN iPS CELLS AND BIO-ENGINEERED SKELETAL MUSCLES. 9th UK Nuclear Envelope Disease and Chrmatin Organisation Meeting / 3rd International Meeting on Laminopathies, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986927⟩
- Tyler J. Kirby, Ashley J. Earle, Gregory R. Fedorchak, Philipp Isermann, Jineet Patel, et al.. Mechanically-induced nuclear damage and increased p53 signaling lead to myofiber dysfunction in skeletal muscle laminopathies. 9th UK Nuclear Envelope Disease and Chrmatin Organisation Meeting / 3rd International Meeting on Laminopathies, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986939⟩
- Daniel J. Owens, Martina Fischer, Kamel Mamchaoui, Sophie Moog, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Nuclear export of YAP requires functional LINC complexes in skeletal muscle. Satellite Meeting European Network for Laminopathies Meeting, Sep 2019, London, United Kingdom. ⟨hal-03986932⟩
- Veronique Bolduc,, Reghan Foley, A., Herimela Solomon-Degefa,, Apurva Sarathy,, Sandra Donkervoort,, et al.. A Common Deep Intronic Mutation Causing Collagen VI-Related Muscular Dystrophy: Validation of Splice-Modulating Approaches In Vitro and Development of a Mouse Model. 22nd Annual Meeting of the American-Society-of-Gene-and-Cell-Therapy (ASGCT), Apr 2019, Washington, DC, United States. Molecular Therapy, 27 (4S1), pp.304, 2019, ⟨10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.04.004⟩. ⟨hal-03997046⟩
- Enzo Cohen, Isabelle Nelson, Valérie Allamand, Maud Beuvin, Corine Gartioux, et al.. The SOLVE-RD project: sharing patients’ data to diagnose rare diseases. 6th International meeting of Myology - Myology 2019, Mar 2019, Bordeaux, France. ⟨hal-03986811⟩
- Anne T. Bertrand, Astrid Brull, Feriel Azibani, Bruno Cadot, Monika Zwerger, et al.. Maintenance of nucleoplasmic lamin A/C during myoblast differentiation induces nuclear fusion in LMNA-related congenital myopathy. 6th International meeting of Myology - Myology 2019, Mar 2019, Bordeaux, France. ⟨hal-03986752⟩
- Elena Gargaun, Rabah Ben Yaou, Marine Guibaud, Guilhem Solé, Vincent Tiffreau, et al.. Phenotypic and genomic characterization of Becker dystrophy patients with 45 to 55 exons deletion. Sixth internatinal congress of myology Myology2019, Mar 2019, Bordeaux (France), France. ⟨hal-04015218⟩
- Astrid Brull, Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Feriel Azibani, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Gene therapy for LMNA-related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy (L-CMD). 6th International meeting of Myology - Myology 2019, Mar 2019, Bordeaux, France. ⟨hal-03986729⟩
- Xavière Lornage, Raphaël Schneider, Chrystel Chéraud, Edoardo Malfatti, Vanessa Schartner, et al.. Myocapture: a large-scale sequencing project to identify novel genes for myopathies. Myologie 2019, Mar 2019, Bordeaux, France. ⟨hal-04029248⟩
- Elena Gargaun, Rabah Ben Yaou, Guilhem Solé, Vincent Tiffreau, Pascale Laforet, et al.. Caractérisation phénotypique et génomique des patients Becker avec délétion des exons 45-55. 29ème Congrès de la Société Française de Neurologie Pédiatrique, Jan 2019, Strasbourg (FRANCE), France. ⟨hal-04015227⟩
- F Azibani, A Brull, L Arandel, M Beuvin, I Nelson, et al.. Gene therapy via trans-splicing for LMNA-related congenital muscular dystrophy. Conference on Changing the Face of Modern Medicine - Stem Cell and Gene Therapy, Oct 2018, Lausanne, Switzerland. Hum. Gene Ther., 29 (12), pp.A138. P379, 2018. ⟨hal-03983935⟩
- Jr. Hogrel, C. Chéraud, I. Ledoux, G. Ollivier, R. Ben Yaou, et al.. The diagnostic value of hyperCKemia induced by the non-ischemic forearm exercise test. 25th International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2018, Mendoza (Argentina), France. 28, pp.S138, 2018, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2018.06.406⟩. ⟨hal-04015249⟩
- E. Malfatti, R. Avila-Polo, X. Lornage, I. Nelson, J. Nectoux, et al.. Loss of sarcomeric scaffolding as a common baseline histopathologic lesion in titin-related myopathies. 23rd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2018, Mendoza, Argentina. Neuromuscular Disorders, 28, pp.S104-S105, 2018, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2018.06.289⟩. ⟨hal-03973451⟩
- I. Nelson, W. de Ridder, B. Asselbergh, B. de Paepe, M. Beuvin, et al.. BVES loss-of-function mutations in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2X with cardiac conduction disorders. 23rd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2018, Mendoza, Argentina. Neuromuscular Disorders, 28, pp.S59-S60, 2018, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2018.06.128⟩. ⟨hal-03973447⟩
- Megan A. Waldrop, Rabah Ben Yaou, Karin K. Lucas, Ann Martin, Erin O’rourke, et al.. Clinical phenotypes as predictors of DMD exon 51 skipping therapy: a systematic review. 2018 New Directions in Biology and Disease of Skeletal Muscle Conference, Jun 2018, New Orleans, Louisiane, United States. ⟨hal-04015230⟩
- V. Sardone, J. Domingos, S. Torelli, A. Jones, M. Ellis, et al.. Dystrophin quantification in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation between dystrophin protein and clinical phenotype. 11th UK Neuromuscular Translational Research Conference, Apr 2018, Cambridge, United Kingdom. Neuromuscular Disorders, 28, pp.S7-S8, 2018, ⟨10.1016/S0960-8966(18)30310-9⟩. ⟨hal-03973445⟩
- Isabelle Nelson, Maud Beuvin, Rabah Ben-Yaou, Cecile Masson, Anne Boland, et al.. Nouvelle mutation d’épissage du gène POPDC1 (BVES) associée à des blocs de conduction cardiaque du 1er degré et une dystrophie musculaire. 9èmes Assises de génétique humaine et médicale, Jan 2018, Nantes, France. . ⟨hal-03986833⟩
- K Piekarowicz, M Beuvin, M Machowska, A Bertrand, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. A muscle hybrid promoter provides specific and effective gene expression after intramuscular and systemic delivery with AAV. European-Society-of-Gene-and-Cell-Therapy (ESCGT) Congress, Oct 2017, Berlin, Germany. Hum. Gene Ther., 28 (12), pp.A44-A45. P096, 2017. ⟨hal-03983944⟩
- R. Rossi, C. Scotton, P. Barton, R. Buchan, R. Walsh, et al.. POPDC1 gene mutation screening in patients with LGMD and heart disturbances: a mutation load effect?. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S140, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.173⟩. ⟨hal-03973396⟩
- A. Reghan Foley, S. Donkervoort, V. Bolduc, Y. Hu, B. Cummings, et al.. A common COL6A1 deep-intronic pseudo-exon inserting mutation causes a distinct phenotype of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2017, Saint-Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S106, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.055⟩. ⟨hal-03996972⟩
- R. Ben Yaou, I. Dabaj, P. Yun, G. Norato, H. Xiong, et al.. First results from the international LMNA -related congenital and childhood onset muscular dystrophy retrospective natural history study. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. 27, pp.S137-S138, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.165⟩. ⟨hal-03973439⟩
- I. Nelson, M. Beuvin, R. Ben-Yaou, C. Masson, A. Boland, et al.. Novel recessive splice site mutation in POPDC1 ( BVES ) is associated with first-degree atrioventricular block and muscular dystrophy. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S139-S140, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.172⟩. ⟨hal-03972940⟩
- C. Macquart, M. Chatzifrangkeskou, M. Gotthardt, Gisèle Bonne, A. Muchir. Abnormal trafficking of connexin 43: A key element in the development of LMNA cardiomyopathy. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S139, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.171⟩. ⟨hal-03973377⟩
- I. Nelson, M. Jacquemont, A. Urtizberea, M. Renouil, A. Boland, et al.. A novel INPP5K mutation in a sibship from the Reunion Island. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S110-S111, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.071⟩. ⟨hal-03973393⟩
- Mathieu Cerino, Svetlana Gorokhova, P. Laforêt, R. Ben Yaou, Emmanuelle Salort-Campana, et al.. Genetic characterization of a French cohort of GNE -mutation negative inclusion body myopathy patients using exome sequencing. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. 27, pp.S149, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.205⟩. ⟨hal-03973434⟩
- I. Dabaj, R. Ben Yaou, C. Bönnemann, A. Nascimento, A. Rutkowski, et al.. Corticosteroid treatment in early-onset lamin A/C related muscular dystrophies. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S138, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.167⟩. ⟨hal-03973411⟩
- M. Kammoun, V. Veksler, J. Piquereau, Gisèle Bonne, M. Beuvin, et al.. TIEG1 is a novel regulator of muscle mitochondrial biogenesis. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S117, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.093⟩. ⟨hal-03973380⟩
- M. Saunier, C. Gartioux, M. Beuvin, N. Mougenot, G. Bonne, et al.. Collagen VI deficiency: The heart of the matter. 22nd International Annual Congress of the World-Muscle-Society (WMS), Oct 2017, Saint-Malo, France. Neuromuscular Disorders, 27, pp.S106, 2017, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2017.06.057⟩. ⟨hal-03996987⟩
- M Garibaldi, J Rendu, E Lacene, G Brochier, Maud Bauvin, et al.. Morphological spectrum of RYR1 recessive myopathies: clinical and genetic correlation. Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2017, Saint Malo, France. 2017. ⟨hal-03968355⟩
- M Kammoun, V Veksler, J Piquereau, Gisèle Bonne, I Nelson, et al.. Loss of TIEG expression results in defective skeletal muscle structure and function with associated impairment of mitochondrial biogenesis.. Annual Meeting of the American-Society-for-Bone-and-Mineral-Research (ASBMR), Sep 2017, Denver (CO), United States. J. Bone Miner. Res., 32 (Suppl 1), pp.S7-S8. 1024, 2017. ⟨hal-03983941⟩
- Karim Wahbi, Caroline Chong-Nguyen, Vincent Algalarrondo, Henri Marc Becane, Pauline Arnaud, et al.. Association Between Mutation Size and Cardiac Involvement in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. International Myotonic Dystrophy Consortium Meeting IDMC-11, Sep 2017, San Francisco, United States. ⟨hal-04019185⟩
- Daniel Owens, Julien Messeant, G Herledan, Arnaud Ferry, Anne Bertrand, et al.. Nuclear envelope protein lamin A/C is a crucial mechanosensory component for skeletal muscle plasticity. International Congress of Neuromuscular Disorders, Sep 2017, Ottawa, Canada. 2017. ⟨hal-03968419⟩
- Anne T Bertrand, Feriel Azibani, Bruno Cadot, Monica Zwerger, Colin Stewart, et al.. Maintenance of nucleoplasmic lamin A/C during myoblast differentiation induces nuclear fusion in LMNA-related congenital myopathy. 10th European meeting on Intermediate filaments, Jun 2017, Saint Malo, France. ⟨hal-03986879⟩
- R Rossi, C Scotton, M Lorenzo, A d'Amico, G Ricci, et al.. POPDC1 gene mutations screening in laminopathies: possible role as a modifier. 50th European-Society-of-Human-Genetics (ESHG) Conference, May 2017, Copenhagen, Denmark. Eur. J. Hum. Genet., 26 (S), pp.445-446. P10.51C, 2018. ⟨hal-03983938⟩
- Margot Saunier, Corine Gartioux, Maud Beuvin, Nathalie Mougenot, Gisèle Bonne, et al.. Collagen VI deficiency: the heart of the matter. Printemps de la Cardiologie, Apr 2017, Nantes, France. ⟨hal-03996993⟩
- L. Ramanoudjame, C. Rocancourt, J. Laine, L. Lyphout, C. Gartioux, et al.. Collagen VI genes in zebrafish skeletal muscle: Implications for collagen VI-myopathies. 17. International Congress of the World Muscle Society, Oct 2012, Perth, Western Australia, Australia. Elsevier, Neuromuscular Disorders, 22, 908 p., 2012, Neuromuscular disorders. Programme and abstracts. ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2012.06.089⟩. ⟨hal-02749637⟩
Proceedings
- Hubert Smeets, Bram Verbrugge, Xavier Bulbena, Liliya Hristova, Julia Vogt, et al.. European Joint Programme on Rare Diseases workshop: LAMA2-muscular dystrophy: paving the road to therapy March 17–19, 2023, Barcelona, Spain. LAMA2-muscular dystrophy: paving the road to therapy, Neuromuscular Disorders, 36, pp.16 - 22, 2024, ⟨10.1016/j.nmd.2024.01.001⟩. ⟨hal-04546346⟩
Special issue
- Ana Rita Carlos, Valérie Allamand. Editorial: Extracellular matrix in homeostasis and cancer. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 2022, Extracellular matrix in homeostasis and cancer, ⟨10.3389/fgene.2022.1107969⟩. ⟨hal-03968194⟩
- Gisèle Bonne. The Treatabolome, an emerging concept. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 8 (3), pp.337-339, 2021, ⟨10.3233/JND-219003⟩. ⟨hal-03856200⟩
Books
- Allamand V, Laure Bidou. eLS. Wiley, 1, 2001, ⟨10.1002/9780470015902.a0022433.pub2⟩. ⟨hal-03838522⟩
Book sections
- K. Boheler, L. Carrier, Catherine Chassagne, D. de la Bastie, J. Mercadier, et al.. Regulation of myosin heavy chain and actin isogenes expression during cardiac growth. Molecular Mechanisms of Cellular Growth, Springer US, pp.101-107, 1991, ⟨10.1007/978-1-4615-3886-8_13⟩. ⟨hal-04275475⟩
Other publications
- Valérie Allamand. Vers une meilleure détection des variants introniques et autres anomalies d’épissage complexes dans les dystrophinopathies. 2022, pp.39-39. ⟨10.1051/medsci/2022182⟩. ⟨hal-03968248⟩
Preprints, Working Papers
- Sanzana Hoque, Marie Sjögren, Valérie Allamand, Kinga Gawlik, Naomi Franke, et al.. Skeletal muscle regeneration is altered in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. 2024. ⟨hal-04433140⟩
- Hong Joo Kim, Payam Mohassel, Sandra Donkervoort, Lin Guo, Kevin O’donovan, et al.. Specific heterozygous frameshift variants in hnRNPA2B1 cause early-onset oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. 2022. ⟨hal-03790055⟩
- Rafael Kronenberg-Tenga, Meltem Tatli, Matthias Eibauer, Wei Wu, Ji-Yeon Shin, et al.. A lamin A/C variant causing striated muscle disease provides insights into filament organization. 2021. ⟨hal-03270949⟩
Videos
- Gisèle Bonne. Présentation des actions Recherche de la Filière en Santé Maladies Rares Neuromusculaires - FILNEMUS. 2023. ⟨hal-04000635⟩
Our last work on the OJRD
A guide to writing systematic reviews of rare disease treatments to generate FAIRcompliant datasets: building a Treatabolome